Figure 8.
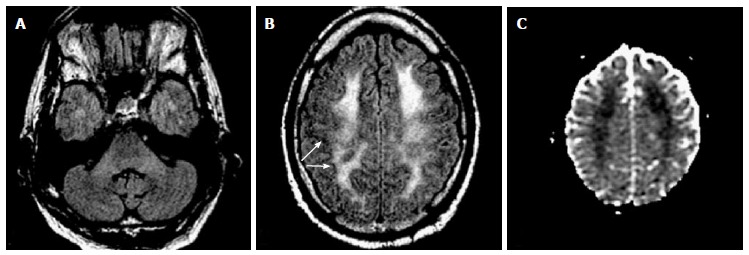
Acute heroin induced leukoencephalopathy (“chasing the dragon”). Twenty-year-old patient found down, history of recent heroin inhalation. A: Axial FLAIR shows subtle increased signal of MCP; Axial FLAIR (B) and ADC maps (C) show concomitant diffuse and confluent increased white matter signal and restricted diffusion with overall sparing of the subcortical u-fibers (arrows on B) and cortex. Though difficult to differentiate from hypoxic-ischemic event, the cortical sparing is more common in toxic leukoencephalopathies. Restricted diffusion has been described not only in the acute stage of toxic heroin inhalation, but in other hypoxic-toxic-metabolic states and could represent acute intramyelinic or excitotoxic edema, in some cases reversible. Evolution could lead to a chronic “chasing the dragon”, spongiform leukoencephalopathy, where the posterior white matter, pons and MCP are typically involved. MCP: Middle cerebellar peduncles.
