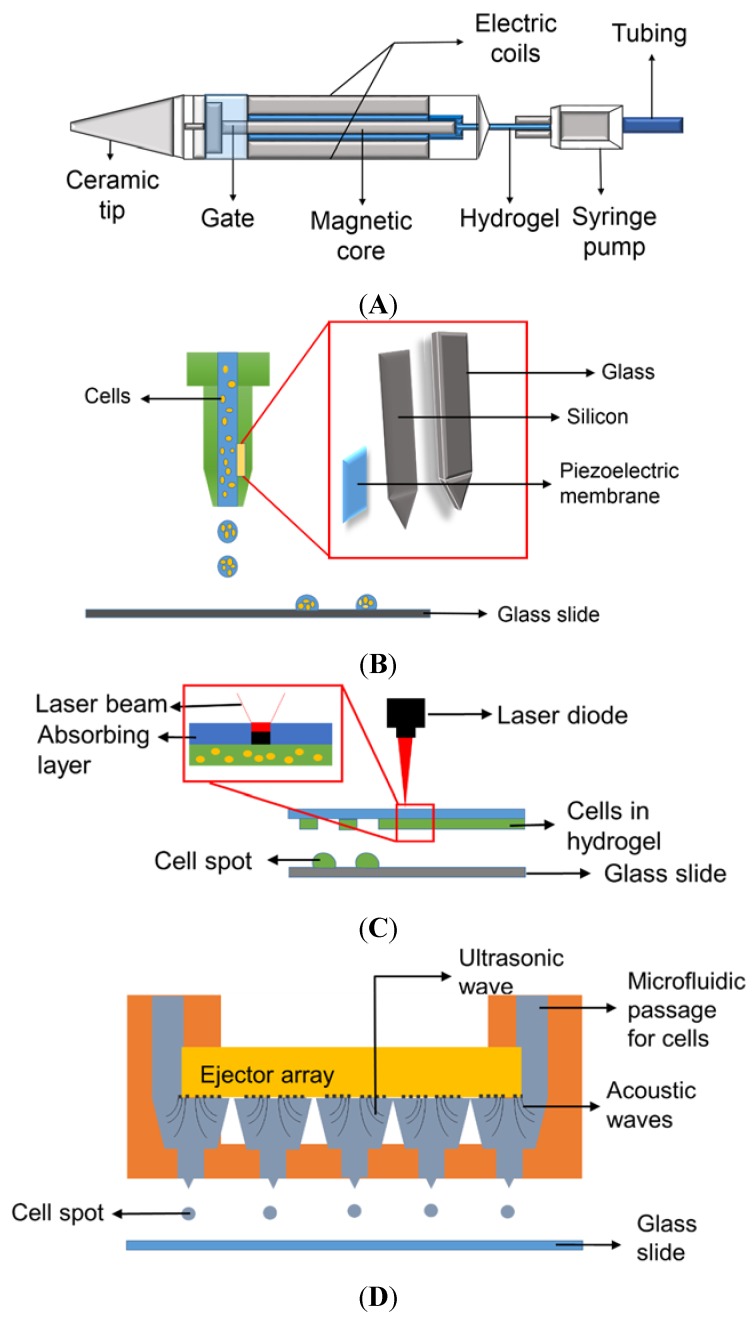
Figure 1.
Various mechanisms for printing biological samples: (A) Micro-solenoid valve using electromagnetic induction; (B) Piezoelectric nozzle using piezoelectric vibration; (C) Laser-induced forward transfer (LIFT) using a laser beam to propel cell spots [13], and (D) Acoustic wave generator using ultrasound to produce acoustic waves for cell printing (Reproduced from Reference [23] with permission of The Royal Society of Chemistry).