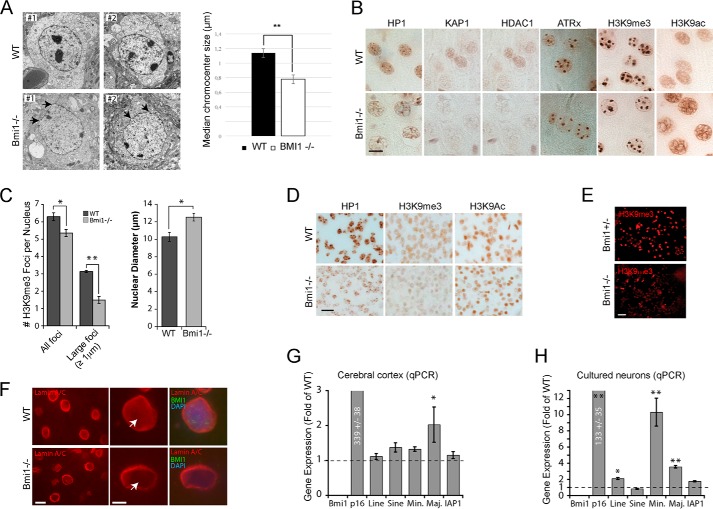
FIGURE 1.
Bmi1-deficient mouse cortical neurons present heterochromatin anomalies. A, transmission electron microscopy analysis of cortical neurons in P30 WT and Bmi1−/− mice. Note the reduction in electron dense chromocenters and the anomalies in nuclear membrane architecture in Bmi1−/− neurons (arrows). B, paraffin-embedded brain sections from P30 WT and Bmi1−/− mice were analyzed by immunohistochemistry. Labeled cells are neurons located in the upper cortical layers of the cerebral cortex. Scale bar, 10 μm. C, quantification of the total number of H3K9me3-positive chromocenter and number of large H3K9me3-positive chromocenters. Note that the nuclear diameter of the neuron is increased in Bmi1−/− mice. Where n = 3 brains for each genotype. *, p < 0.05, **, p < 0.01. D, paraffin-embedded brain sections from e18.5 WT and Bmi1−/− embryos were analyzed as in B. E and F, cultured embryonic cortical neurons (E) and P30 cortical sections (F) were analyzed by immunofluorescence, revealing reduced H3K9me3 and Lamin A/C labeling (arrows) in Bmi1−/− neurons. Scale bars: 40 (E), 10 (F), and 5 μm (F′). G, whole cortices or (H) e18.5 neurons from WT and Bmi1−/− mice were analyzed by qPCR for satellite repeats and intergenic retroelements expression. P16Ink4a was used as positive control. Note the up-regulation of minor and major satellite repeats in Bmi1−/− neurons. Where n = 3 independent samples for each genotype. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01.