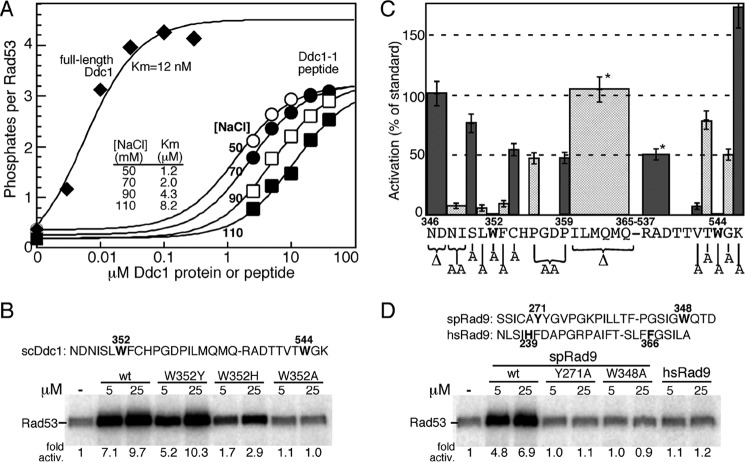
FIGURE 2.
Activation of Mec1 by Ddc1- and Rad9-derived peptides. A, titration of full-length Ddc1 (at 50 mm NaCl) or the Ddc1-1 peptide (sequence given in B) at varying NaCl concentrations in the standard Mec1 assay with Rad53-kd as substrate (see “Experimental Procedures”). Data are modeled to standard Michaelis-Menten kinetics, and the Km values are shown. B, activity of wild-type Ddc1-1 peptide and the indicated variants. The Ddc1-1 peptide sequence is shown, with amino acid positions corresponding to the full-length protein. The two essential tryptophans are in bold. C, various residues or groups of residues in the Ddc1-1 peptide were deleted or mutated to alanine, as indicated in the graph, and their ability to stimulate Mec1 was quantified relative to the wild-type peptide. Peptide concentrations ranged from 5–50 μm. Data represent the average of at least three independent experiments for peptides that showed activity, and of two experiments for peptides that were inactive. Error bars are standard error of the mean. Pro-356 and Pro-359 were simultaneously mutated to alanines. * indicates that the ILMQMQ and RAD deletions were made in a peptide that also had ND346,347 deleted. D, S. pombe Rad9-derived wild-type and variant peptides and a human Rad9-derived peptide were tested in the same assay.