FIGURE 2.
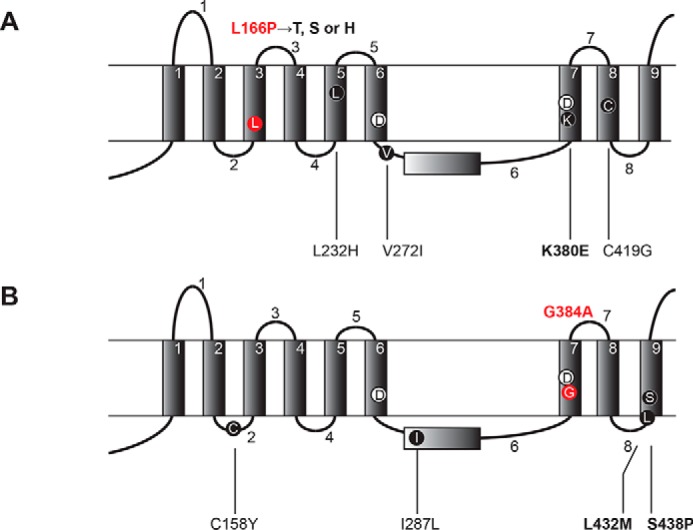
FAD mutations and secondary suppressor mutations map to the transmembrane and loop domains of PS1. FAD mutation (L166P or G384A) and secondary suppressors (A and B) are shown. PS1 models with the nine transmembrane domains (TMD) 1–9 and the eight loop domains 1–8 (13–15) are shown. The suppressor mutations for L166P (red) include the primary mutation K380E together with three variable mutations (L232H, V272I and C419G) (A). The suppressor mutations for G384A (red) include the primary mutation L432M or S438P with secondary mutation C158Y or I287L, respectively (B). The critical secondary mutations are indicated in boldface and the FAD mutations are in red. Catalytic Asp residues in TMD6 and TMD7 (Asp-257 and Asp-385) are also indicated.
