Figure 4 .
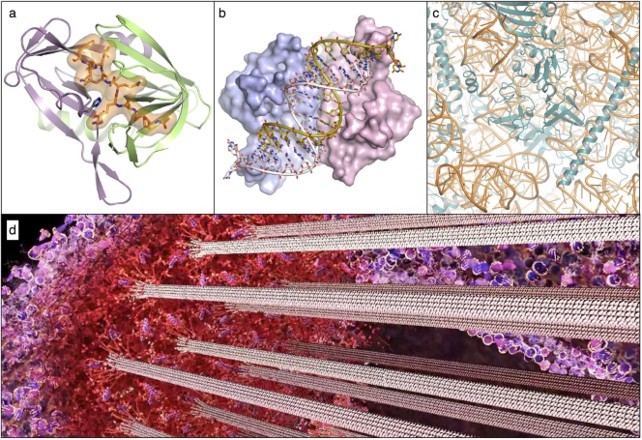
Molecular structures and the molecular sociology of the cell: (a) interaction between the foot-and-mouth disease 3C protease and a peptide it is about to cleave (PDB ID 2wv4) (Zunszain et al. 2010), (b) structure of tomato aspermy virus protein 2b bound to and neutralizing the antiviral effect of a cellular double-stranded RNA molecule (PDB ID 2zi0) (Chen et al. 2008), (c) close-up view of the ribosome, the gigantic RNA-protein machine that synthesizes proteins found in all cells (PDB ID 4v88) (Ben-Shem et al. 2011), (d) detail from a still from the animation ‘Chromosome and Kinetochore’. (https://youtu.be/0JpOJ4F4984) showing the kinetochore and associated microtubules, a complex system of molecules that separates duplicated chromosomes just prior to cell division.
