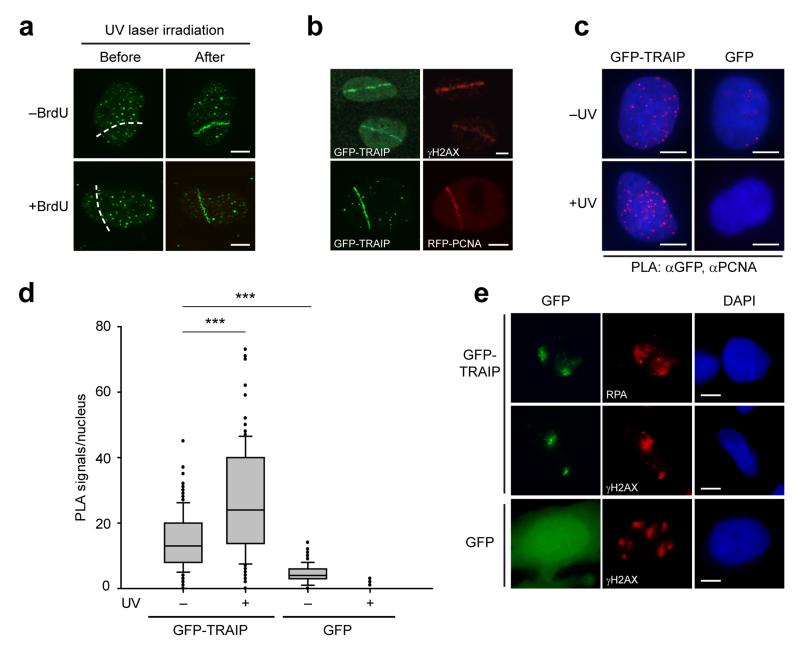
Figure 3. TRAIP localizes to sites of UV-induced DNA damage.
(a) TRAIP localizes to DNA damage sites induced by UV laser microirradiation both in the absence and presence of pre-treatment with BrdU as a damage sensitizer. Representative images, before and after UV laser microirradiation. Scale bar, 5 μm. (b) GFP-TRAIP colocalizes with γH2AX and with RFP-PCNA at sites of UV laser-induced damage. Representative images of UV laser-irradiated GFP-TRAIP expressing cells immunostained for γH2AX (pre-sensitized with BrdU) or co-expressing RFP-PCNA (no BrdU pre-treatment) as indicated. Scale bar, 5 μm. (c, d) GFP-TRAIP is detected by a Proximity Ligation Assay (PLA) in close proximity to PCNA, an association enhanced after UV-induced damage. (c) Representative images of PLA signals/nucleus in doxycycline-inducible GFP-TRAIP HeLa cells before and after damage with 25 J/m2 UV-C. Scale bar, 5 μm. (d) Quantification of PLA signals/nucleus. Box plots, center line denote mean values, box 25/75 %, whiskers 5/95 %, data pooled from n=2 independent experiments, n>65 data points per condition per experiment; Mann Whitney rank sum test: *** p<0.001. (e) TRAIP accumulates at sites of localized UV damage, colocalising with RPA and γH2AX. Representative immunofluorescence images of MRC5 cells transfected with GFP-TRAIP or GFP alone after UV-C irradiation through 3 μm microfilters. Scale bar, 5 μm.