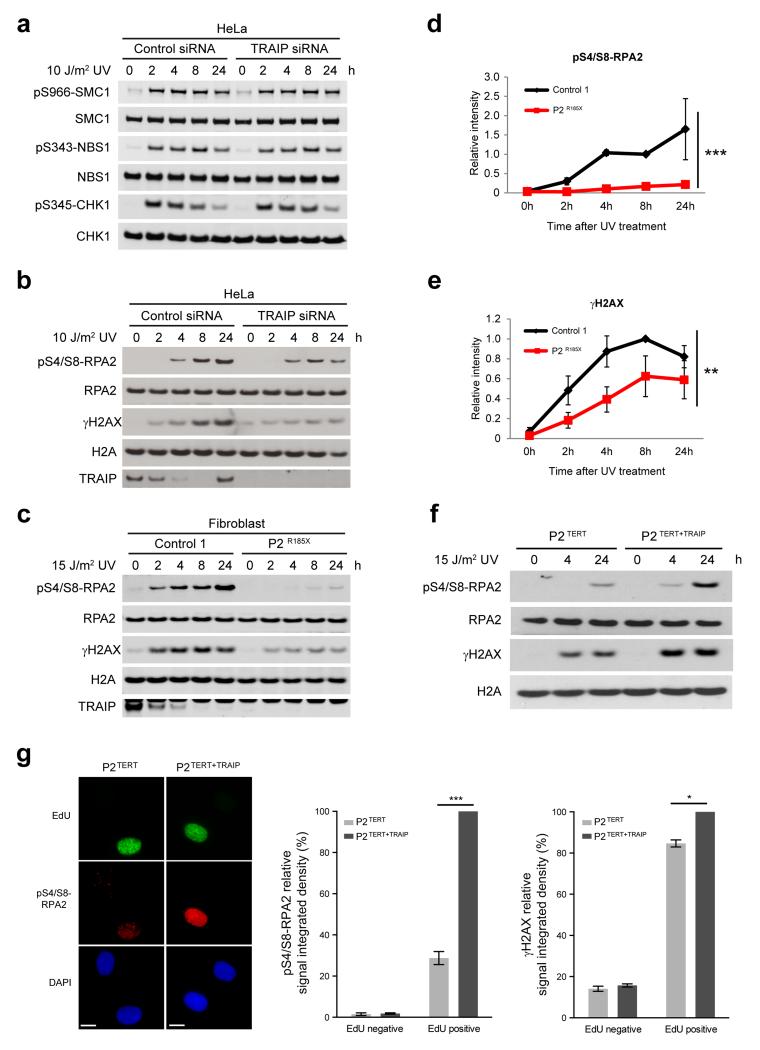
Figure 4. TRAIP is required for UV-induced RPA2 and H2AX phosphorylation during S-phase.
(a) Phosphorylation of downstream ATR substrates is unaffected by TRAIP depletion. HeLa cells were transfected with RNAi against TRAIP or luciferase (control). After 72h, cells were UV-C treated, before harvesting at indicated times. Cell lysates were analyzed by Western blot as indicated. (b, c) TRAIP loss reduces RPA2 phosphorylation and histone H2AX phosphorylation (γH2AX) in response to UV. HeLa cells transfected with TRAIP and control siRNAs (b) or primary patient fibroblasts (c) were UV-C treated, harvested and immunoblotted as indicated. (d, e) Quantification of pS4/S8-RPA2 (d) and γH2AX (e) in primary fibroblasts after UV. Chemiluminescence from Western blots quantified using ImageQuant. Mean ± SEM, n=3 experiments; values normalized to total RPA2 signal; two-way ANOVA across all time points: *** p<0.001, ** p<0.01. (f) Retroviral complementation with wild-type TRAIP rescues impaired phosphorylation of RPA2 and H2AX after UV-C irradiation in TRAIPArg185* cells. Fibroblasts derived from P2Arg185* were immortalized with hTERT, denoted P2TERT; and reconstituted with pMSCV-TRAIP, P2TERT+TRAIP. (g) TRAIP is required for optimal RPA2 and H2AX phosphorylation in S-phase. P2TERT and P2TERT+TRAIP cells were irradiated with 15 J/m2 UV-C, labeled with EdU for 4 h, pre-extracted, fixed and co-stained for pS4/S8-RPA2 or γH2AX, EdU and DAPI. Representative images of immunofluorescence staining of pS4/S8-RPA2 (left), quantification of pS4/S8-RPA2 (middle) and γH2AX (right) signal integrated density in EdU-positive and EdU-negative cells. Mean ± SEM for n=3 experiments, values normalized to P2TERT+TRAIP; Student’s t-test: *p<0.05; ***p<0.001. Scale bar, 10 μm.