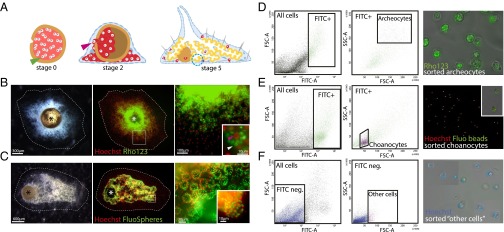
Fig. 1.
Staining of cells from juvenile Ephydatia and FACS sorting of archeocytes, choanocytes, and other cells. (A) Gemmule hatching process. Blue dotted circle, choanocyte chamber; green arrowhead, thesocyte; pink arrowhead, archeocyte. (B) Stage 2 juvenile E. fluviatilis (Left), Hoechst 33342 and Rho123 counterstaining (Middle), and magnified archeocytes (Right) containing Rhodamine-stained vitelline platelets (Inset, white arrowhead) and a large nucleolated nucleus (Inset, red arrowhead). (C) Stage 5 juvenile E. fluviatilis (Left), Hoechst 33342 and FluoSphere counterstaining (Middle), and magnified stained choanocyte chambers (Right and Inset) containing fluorescent beads (green). Asterisks in B and C indicate the gemmule coat. (D) FACS gate for archeocytes (Left panels) and photograph showing purified cells (Right panel) (large size and strong green fluorescence). (E) FACS gate for choanocytes (Left panels) and photograph showing purified cells (Right) (small size and strong green fluorescence). Inset shows two choanocytes with several ingested fluorescent beads. (F) FACS gate for other cells (Left panels) and purified cells (Right) (heterogeneous size and weak or no green fluorescence). Note that several fields have been combined to show the heterogeneity of cell sizes in that fraction. FITC-A, green fluorescence; FSC-A, forward scatter; SSC-A, side scatter.