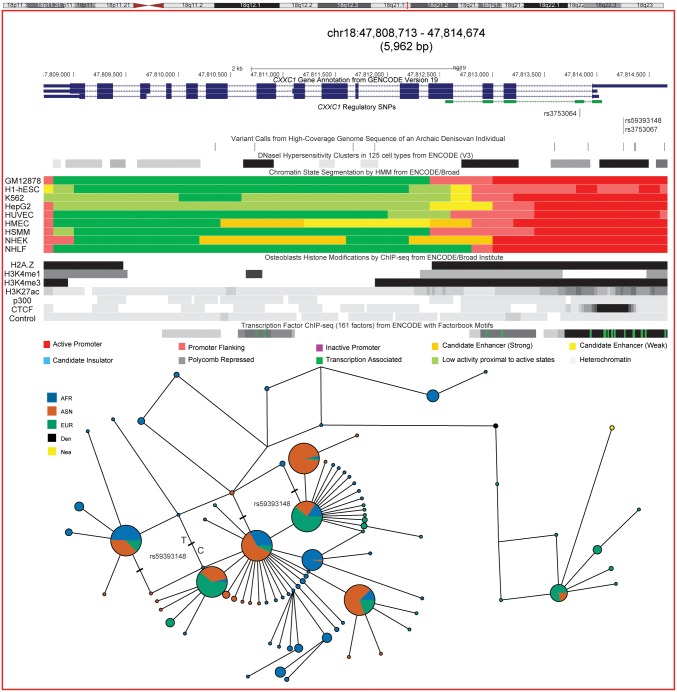
Fig 3. Positive selection at the CXXC1 locus.
A ~6 kb region on chromosome 18 that spans CXXC1 showing GENCODE (Version 19) transcript annotation. The three short-listed candidate regulatory variants driving the selection signal in East Asians are all located in ENCODE annotated regions of open chromatin, depicted in the DNase I Hypersensitivity Clusters in 125 cell lines track, and show ENCODE chromatin state segmentation associated with an active promoter site in nine human cell lines. The latter include lymphoblastoids [GM12878]; embryonic stem cells [H1-hESC]; chronic myelogenous leukemia [K562]; hepatocellular carcinoma [HepG2]; umbilical vein endothelial [HUVEC]; mammary epithelial [HMEC]; skeletal muscle myoblast [HSMM]; skin epidermal keratinocytes [NHEK] and lung fibroblasts [NHLF]). Positions of histone modifications in osteoblasts are indicated by shaded bands and the black shade signifies enrichment. In osteoblasts the position of the histone sequence variant, H2A.Z, that determines accessibility of the transcription start site (TSS) and histone modifications like H3K4me3 that are enriched around TSS (dark bands) encompasses the candidate regulatory variant site and show binding for many transcription factors. H3K4me1 and H3K27ac modifications and p300 marks are enriched around active enhancers and CTCF indicates insulator regions. The lower part of the figure shows median joining haplotype networks in this region that is in high LD (r2 ≥ 0.95) in CHB. Phased haplotypes generated by the 1000 Genomes Project were used to construct this network. The derived C allele for the regulatory variant rs59393148 lies on the branch leading towards the most frequent haplotype found in East Asians, and shows a star like expansion typical of a selection signal. Note the proximity of archaic human haplotypes with a subset of East Asian (ASN) and European Finnish samples. These samples lie on a divergent branch that is closer to the Neanderthal (Nea) and Denisovan (Den) haplotype when compared with the rest of the modern human population samples.