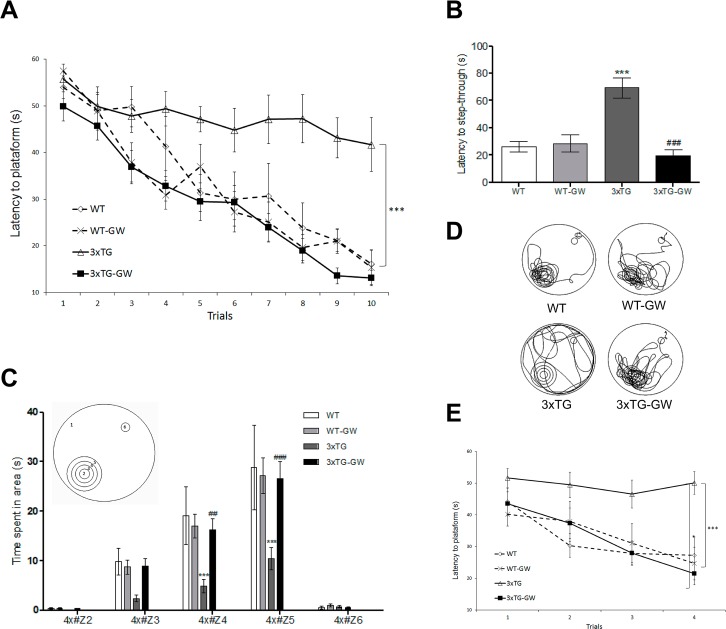
Fig 1. LXR agonist restores memory and cognition in the 3xTg-AD mice.
Spatial learning and memory were evaluated by means of the MWM after 12 weeks of treatment with the LXR agonist GW3965. (A) Learning task: treated 3xTg-AD mice took significantly less time to learn the location of the hidden platform. Statistical significant differences were found by using two-way ANOVA. *** p<0.001. (B-D) Retention tasks: (B) latency to step-through place of platform in seconds. Significant differences were found by using ANOVA followed by Tukey's multiple comparison test; (C) 4X analysis: time spent nearest the platform; (D) Representative samples of paths taken during the retention task illustrate the marked preference between treated and untreated WT and 3xTg-AD mice. (E) Reversal learning: treated 3xTg-AD mice took significantly less time to learn the new location of the hidden platform after two days of trials. All data were expressed as mean ± S.E.M. *** represents p < 0.001 compared with WT; ### represents p < 0.001 compared with untreated 3xTg-AD. Cohort sizes were: WT, n = 7; WT treated, n = 10; 3xTg-AD untreated, n = 8; treated 3xTG, (Randomized Females and Males) n = 12. Learning task: all data were expressed as mean ± S.E.M. *** represents p < 0.001, compared with WT; ### represents p < 0.001 compared with untreated 3xTg-AD.