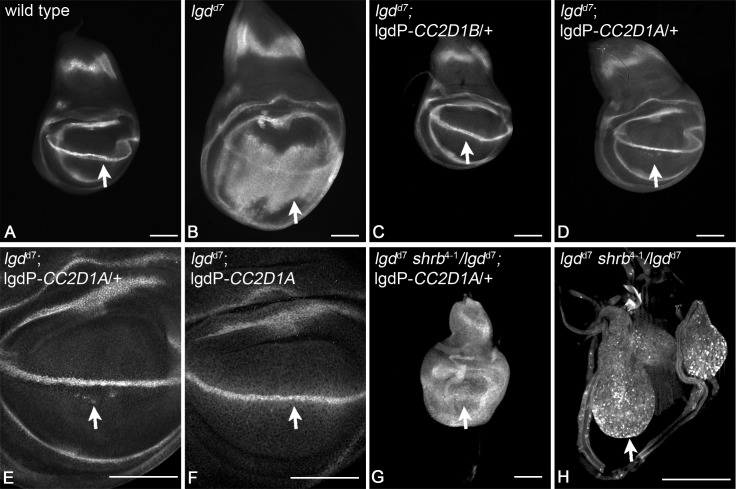
Fig 10. Human CC2D1A and CC2D1B can replace the function of Lgd in D. melanogaster.
(A) Expression of the Notch target gene wingless (Wg) in a wild type wing imaginal disc. (B) Expression of Wg in an lgd null mutant disc (lgdd7). The expression domain has broadened dramatically, indicating an expansion of Notch activity. In addition, the disc is much larger due to over-proliferation of the disc cells. Expression of one copy of CC2D1B (C) or CC2D1A (D) normalises the expression of Wg. (E) Magnification of the wing area of the disc shown in (D). It reveals that a few cells still express Wg ectopically indication that the rescue of lgd mutants by CC2D1A is incomplete. (F) The ectopic expression of Wg is completely suppressed if two copies of CC2D1A are present in the genome. (G) The phenotype of lgd mutant discs rescued with one copy of CC2D1A worsened dramatically upon loss of one copy of shrb. (H) The wing imaginal disc of an lgd mutant, shrub heterozygous animal. The animals die during the early third larval instar stage and contain very small imaginal discs with Wg primarily located in dramatically enlarged endosomes. Arrows point to the expression domain of Wg along the dorsoventral boundary, which is controlled by the activity of the Notch pathway. Scale bars are 100μm.