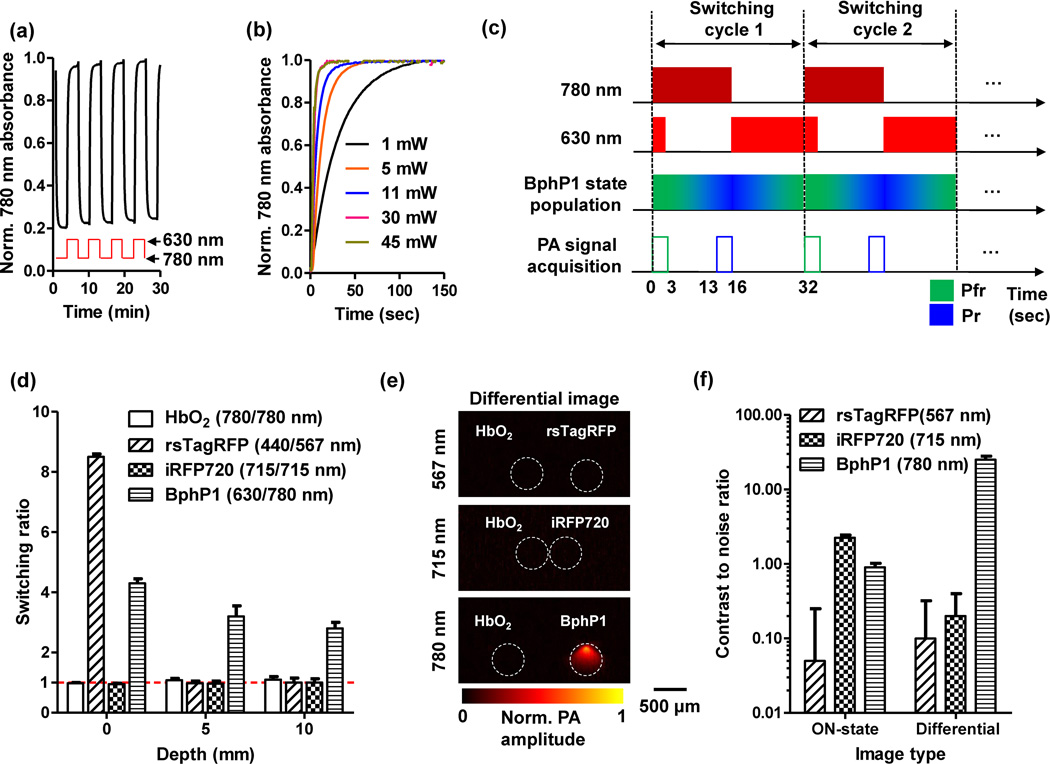
Fig. 2.
Optical and photoacoustic (PA) characterization of reversible photoswitching of BphP1. (a) Absorbance of BphP1 at 780 nm, switched off with 780 nm light illumination and then switched on with 630 nm light illumination. The photoswitching period was 180 seconds for both wavelengths, with an absorbance-rise half-time of 16 seconds and an absorbance-fall half-time of 8 seconds. (b) Switching on rate of BphP1 with 630 nm light illumination at different power levels. (c) Time sequences of the photoswitching cycle of BphP1. The 780 nm light is used for PA imaging and switching off the protein, and. The PA signals are acquired only with the 780 nm illumination. (d) Switching ratio of purified proteins at different imaging depths in scattering media (1% intralipid and 10% gelatin in distilled water; reduced scattering coefficient of ~10 cm−1). We define switching ratio as the ratio between the PA signal amplitudes acquired in the ON and OFF states of the proteins. Error bars, s.d. (e) Differential PA images of the purified proteins at 10 mm depth, acquired at their respective wavelengths. HbO2 was imaged with each protein to provide a reference. (f) Comparison of the contrast to noise ratio quantified from the ON state images and the differential images. Error bars, s.d.