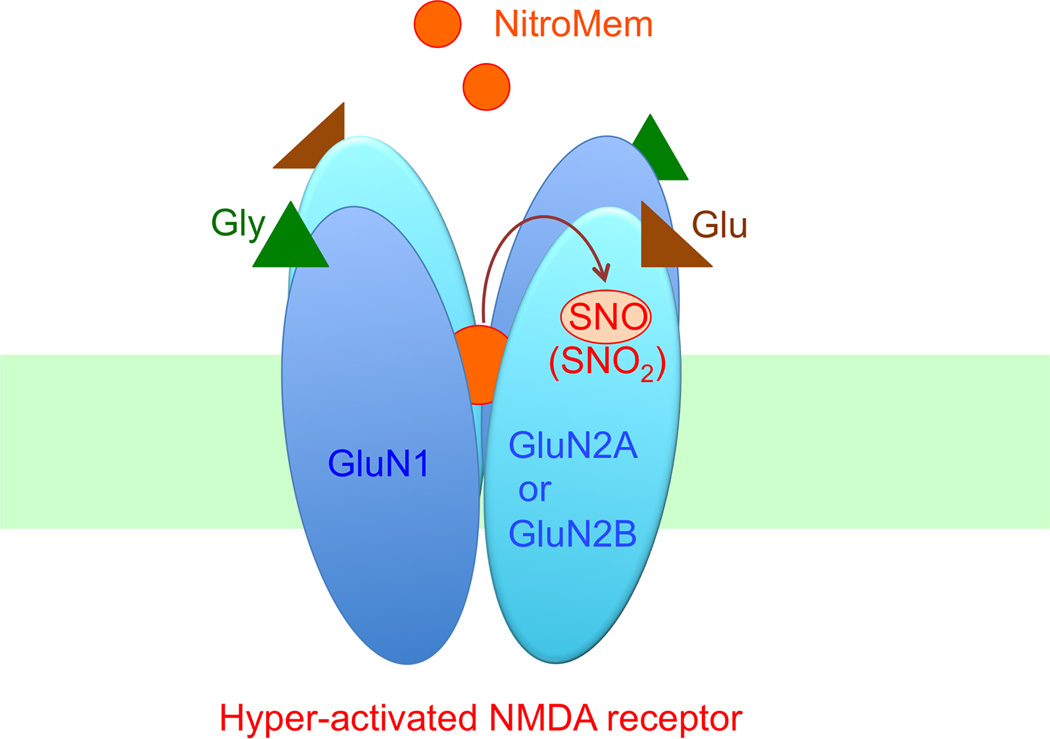
Figure 3.
NitroMemantine-mediated inhibition of hyperactivated NMDA receptors. NitroMemantine was synthesized by addition of a nitro group (-NO2) to the memantine moiety. This allows NitroMemantine to antagonize excessively activated NMDA receptors via two sites of action: 1) the ion channel where memantine itself binds, and 2) an extracellular redox-sensitive cysteine thiol groups of the receptor where the nitro group reacts to inhibit NMDAR activity (forming –SNO or –SNO2). Thus, in this scenario, NitroMemantine serves as an NO (or, more precisely, a nitro group) donor specifically targeting NMDA receptors. This figure also shows that the NMDA receptor is a heterodimer, composed of two GluN1 and two GluN2 subunits. Excessive concentrations of glycine (Gly) and glutamate (Glu), co-agonists of the receptor, can trigger pathological activation of the NMDA receptor.