Fig. 7.
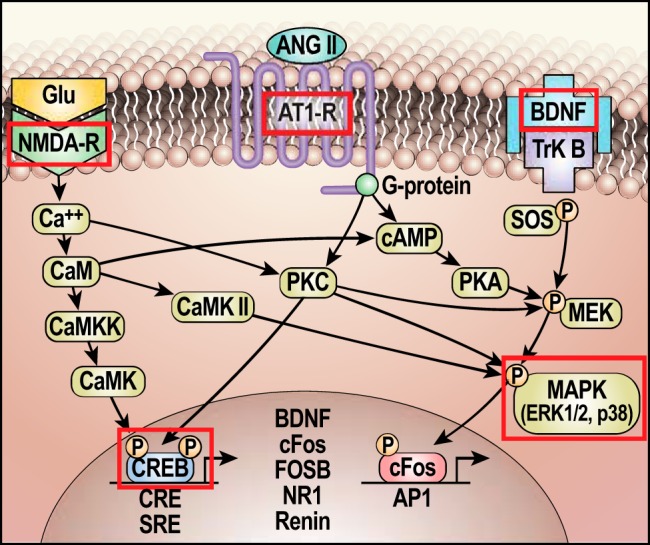
Schematic of hypothesized molecular mechanisms involved in neuroplasticity underlying the sensitization of hypertension by prior experience. Outlined in red are components found to have sustained changes at the end of the delay period following the induction of sensitization of the hypertensive response. Glu, glutamate; CaM, calmodulin; CaMK II, Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent kinase II; CaMKK, calmodulin-dependent protein kinase kinase; CaMK, Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase; AT1R, angiotensin type 1 receptor; CRE, cAMP response element; CREB, CRE-binding protein; cAMP, cyclic adenosine monophosphate; BDNF, brain-derived neurotrophic factor; ERK1/2, extracellular signal regulating kinase; TrkB, tropomyosin-related kinase B; SOS, son of sevenless (guanine nucleotide exchange factor); SRE, serum response element; MEK, MAP kinase kinase (a.k.a. MAPKK); MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; c-Fos, FOSB, FBJ murine osteosarcoma viral oncogene homolog B; AP1, activator protein 1; PKA, protein kinase A; NMDA-R, a glutamate ionotropic receptor; ANG II, angiotensin II; NR1, NMDA-R subunit.
