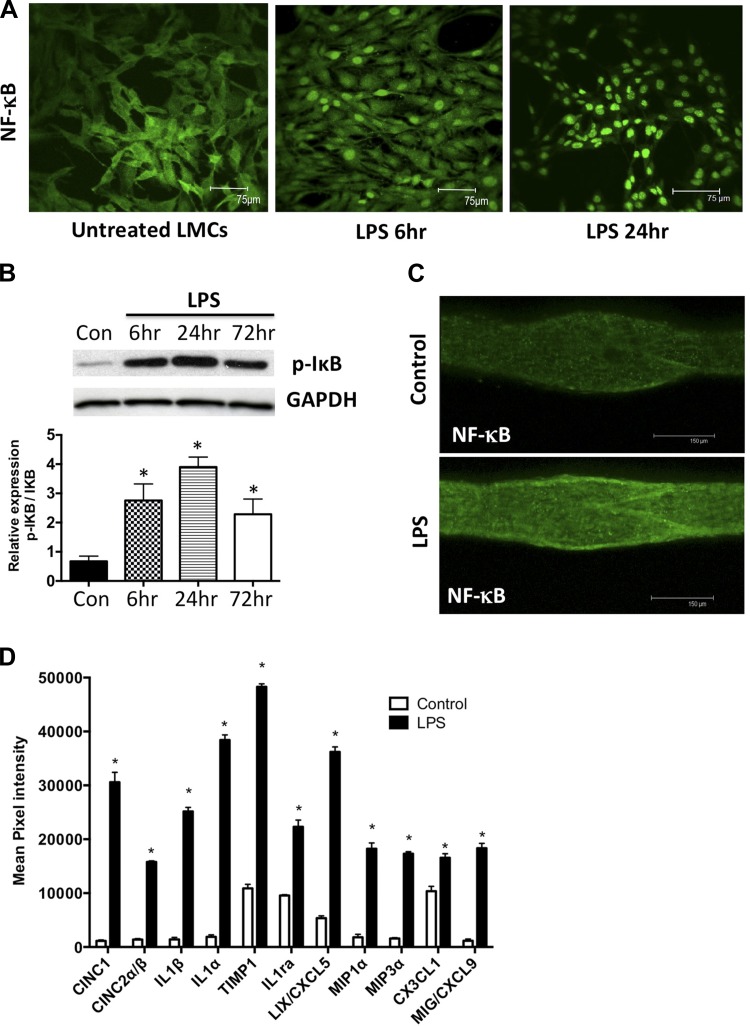
Fig. 7.
LPS causes activation of the NF-κB and proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines in the lymphatics. A: LPS activates NF-κB in cultured mesenteric LMCs. LMCs were treated with LPS (20 ng/ml) for 6 h and 24 h, and nuclear translocation of NF-κB was assessed using immunofluorescence. Magnification is ×20. B: LPS activates I-κB in cultured mesenteric LMCs. LMCs were treated with LPS (20 ng/ml) for 6, 24, and 72 h, and Western blot analysis was carried out. Magnification is ×20. C: LPS activates NF-κB in mesenteric lymphatic vessels. Mesenteric lymphatic vessels isolated from a 6-h LPS-treated rat were assessed for nuclear translocation of NF-κB using immunofluorescence. Magnification is ×20. Scale bar: 150 μm. D: LPS induces the expression of several cytokines and chemokines in lymphatic mesenteric tissue arcades. Proteins isolated from mesenteric tissue arcades from untreated and LPS-treated animals were analyzed by inflammatory cytokine array. Mean pixel density of each analyte was quantified and plotted and represented as fold change over control. Data are represented as means ± SE. B and D: *P < 0.05; n = 3.