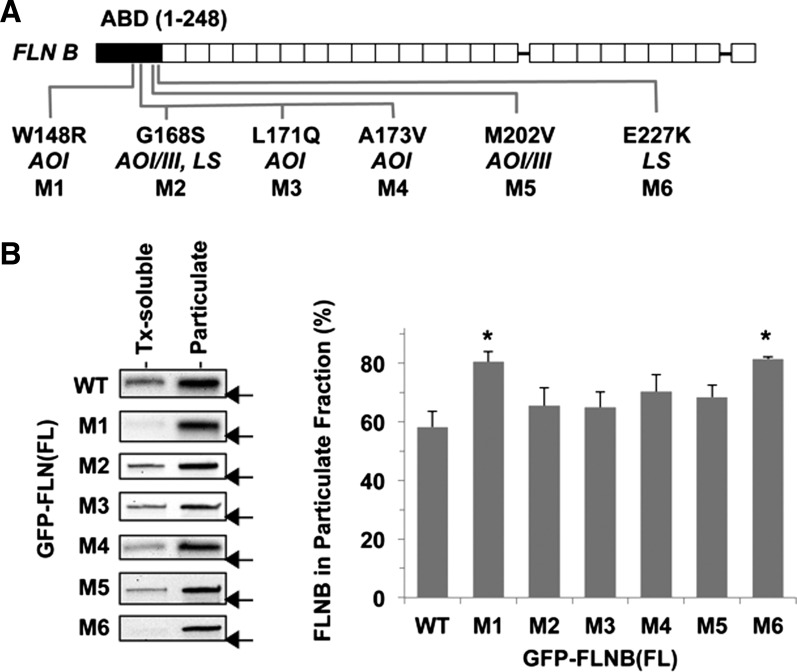
Fig. 1.
Subcellular fractionation of cells expressing the pathological variants of human filamin B (FLNB). A: human FLNB structure. Amino acid substitutions that have been linked to the genetic disorders atelosteogenesis types I and III (AOI and AOIII) and Larsen's syndrome (LS), M1–M6, are shown below the human FLNB structure. Solid and open boxes indicate actin-binding domain (ABD) and immunoglobulin-like repeats, respectively. B: each of 7 green fluorescent protein (GFP)-tagged full-length (FL) FLNB proteins, wild-type (WT) and M1–M6, was transiently expressed in HEK-293 cells and subjected to subcellular fractionation assay. GFP-FLNB in Triton X-100 (Tx)-soluble and -insoluble (particulate) fractions was detected by immunoblotting using anti-GFP antibody (left), and the percentage of FLNB in the particulate fraction was determined by densitometry (right). Values are means ± SE; n = 3. *P < 0.05 vs. WT (by ANOVA with Dunnett's post hoc test). Arrow indicates the position of a 250-kDa marker on each blot.