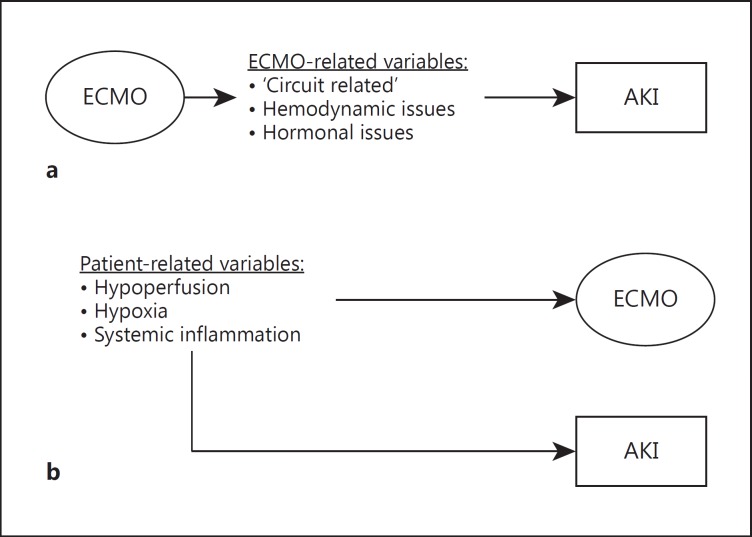
Fig. 1.
Relationship between ECMO and AKI. a Variables directly derived from ECMO therapy may cause AKI; in this hypothesis, ECMO contributes to maintaining kidney dysfunction and causally participates in the development of AKI. b Pretreatment variables or variables which lead to ECMO initiation may also cause AKI development; in this hypothesis, AKI is an epiphenomenon of ECMO and derives from ECMO-independent variables. Theoretically, a third hypothesis may be presented, in which patients with AKI may further require ECMO initiation (e.g. for a cardiorenal syndrome type 3), but this hypothesis is beyond the intention of this review.