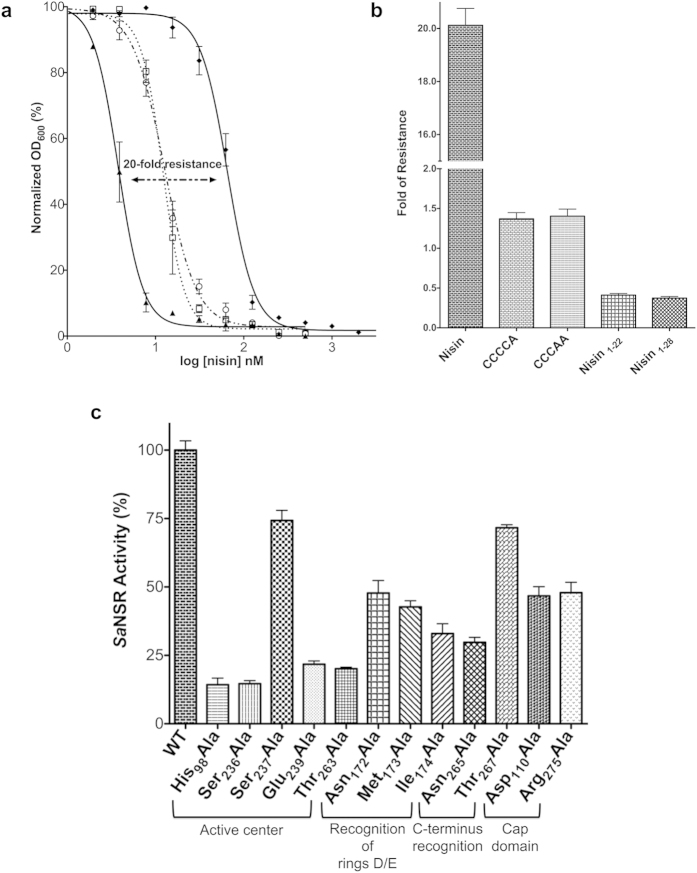
Figure 3. Influence of wild type SaNSR and its mutations against nisin and its variants.
(a) Growth inhibition experiment of SaNSR with nisin. The activity of SaNSR is determined using the L. lactis NZ9000 strain, where the plasmid encoding the SaNSR wildtype and the mutations were transformed, and the IC50 against nisin was determined. As a control, the empty vector was transformed and used in the IC50 study (termed NZ9000Erm). Black lines represent the NZ9000Erm (filled Δ) and NZ9000-SaNSR (♦) strains, respectively. The black dotted lines represent the NZ9000-SaNSR-His98Ala (☐) and NZ9000-SaNSR-Ser236Ala (Ο) strains. The data were fitted and evaluated as described in ref. 51. The difference in the growth exhibited by the strains was used to calculate the percentage of activity. Each experiment was performed at least in triplicates. (b) Graphical representation of the fold of resistance exhibited by SaNSR with nisin and different nisin variants (CCCCA, CCCAA, nisin1-22 and nisin1-28). The NZ9000Erm and NZ9000SaNSR strains were used to determine the activity of all the nisin variants. The error bars indicate the standard error of at least three independent experiments. (c) The activity of SaNSR and its mutations is determined using the L. lactis NZ9000 strain. A normalization of the IC50 values were done by setting the values exhibited by the empty vector (NZ9000Erm) and NZ9000SaNSR to 0% and 100%, respectively. The error bars indicate the standard error of at least three independent experiments.