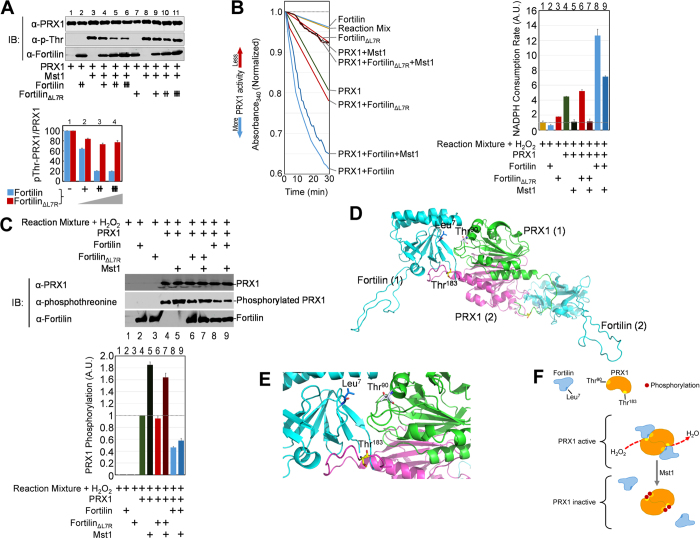
Figure 3. Fortilin prevents Mst1 from phosphorylating and deactivating PRX1.
(A). An in vitro phosphorylation assay shows the binding-dependent inhibitory effect of fortilin on PRX1 phosphorylation by Mst1. Abbreviations: IB, immunoblot; α-PRX1, anti-PRX1 antibody; α-p-Thr, anti-phosphothreonine antibody; α-Fortilin, anti-fortilin antibody. Increasing doses of recombinant human fortilin (lanes 3–6), but not its mutant (fortilinΔL7R, lanes 8–11), decreased phosphorylation of PRX1 by Mst1 in vitro. Densitometry was used to quantify the amount of threonine-phosphorylated PRX1. (B). Fortilin, but not fortilinΔL7R, protects PRX1 enzymatic activity from inhibition by Mst1. NADPH, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate; A.U., arbitrary unit. Results are shown as the mean ± SD three independent experiments. (C). Fortilin preserves the enzymatic activity of PRX1 by preventing Mst1 from phosphorylating PRX1. IB, immunoblot; α-phosphothreonine, anti-phosphothreonine antibody; α-Fortilin, anti-fortilin antibody; A.U., arbitrary unit derived from the densitometric ratio of the phosphorylated PRX1 threonine band to the respective total PRX1 band. The means and errors ( ± SD) of the graph were calculated from three independent experiments. (D). The PRX1 dimer interacts with two fortilin molecules. Fortilin occludes the PRX1 Thr183 phosphorylation site on the C-terminal tail of one subunit of the dimer and Thr90 on the second subunit. (E). Interaction facet between fortilin and dimerized PRX1s. (F). A model of physical and functional interaction between dimerized PRX1s and fortilins. Without fortilin, PRX1 is accessible by Mst1 for the phosphorylation of Thr90 and Thr183, key activity-regulating residues of PRX1. See also Fig. S3.