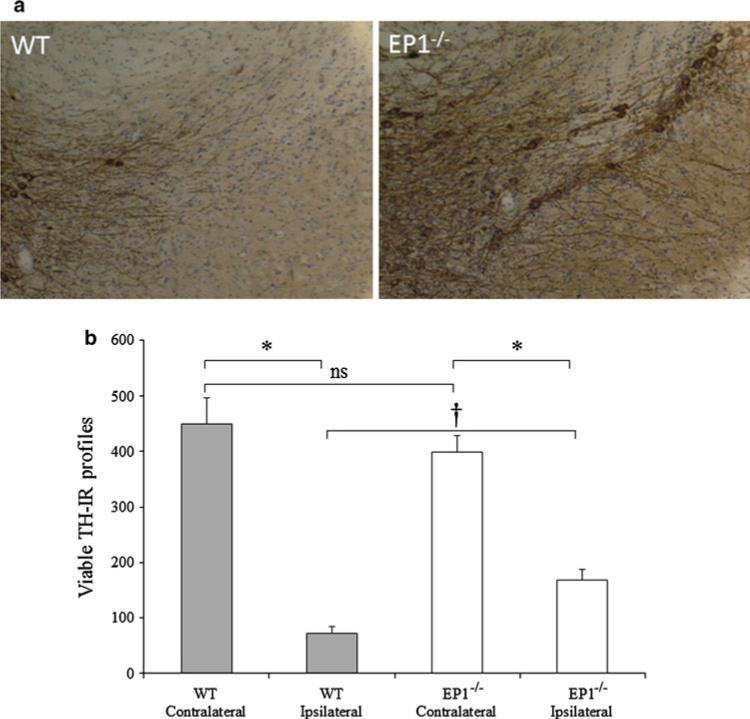
Fig. 2.
EP1 deletion prevents 6-OHDA-induced dopaminergic cell death: On day 8, the 6-OHDA-lesioned mice were transcardially perfused and fixed, and harvested brains were fixed overnight in PFA, then equilibrated with sucrose. Every 4th coronal cryosection of 25 μm from the substantia nigra was processed for TH immunohistochemistry. TH-IR profiles representing dopaminergic neurons in the ipsilateral and contralateral SNpc were manually counted in each section at ×40. a Representative sections at ×10 showing TH-IR profiles in the SNpc in WT ipsilateral (left panel), and EP1−/− ipsilateral (right panel) sections. b Histogram showing the total number of TH-IR profiles in each hemispheric SNpc of WT and EP1−/− mice. Quantification of the TH-IR profiles shows significant protection of the dopaminergic cells in the EP1−/− ipsilateral SNpc. There was 47.68 ± 8.08 % protection in the EP1−/− group as compared with the WT group. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. *p < 0.001 as compared with the WT or EP1−/− contralateral SNpc. †p < 0.05 as compared with the WT ipsilateral SNpc. There was no significant (ns) difference between the contralateral side of WT and EP1−/−