Figure 4.
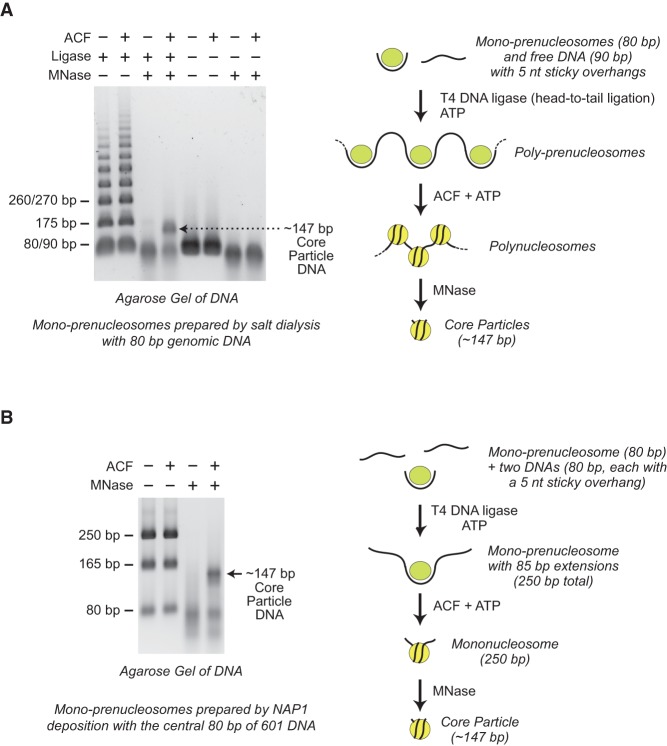
Prenucleosomes can be converted into canonical nucleosomes by ACF. (A) ACF-dependent assembly of poly-prenucleosomes to polynucleosomes. Mono-prenucleosomes (prepared by salt dialysis with 80-bp genomic DNA containing two 5-nt overhangs) were ligated in a sequential head-to-tail fashion with free DNA (90 bp with two 5-nt overhangs) to give poly-prenucleosomes, as indicated in the diagram. The resulting poly-prenucleosomes were assembled into polynucleosomes with ACF and ATP. The formation of canonical nucleosomes was verified by MNase digestion of the polynucleosomes into core particles, which contain ∼147 bp of DNA. (B) ACF-dependent assembly of mono-prenucleosomes to canonical nucleosomes. Mono-prenucleosomes (prepared by NAP1-mediated histone deposition with the central 80 bp of 601 DNA containing two 5-nt overhangs) were ligated to two free 80-bp DNA fragments (each containing a single 5-nt overhang) to give mono-prenucleosomes that are flanked by 85-bp DNA extensions, as illustrated in the diagram. The resulting mono-prenucleosomes were assembled into nucleosomes by ACF. The formation of canonical nucleosomes was assessed by MNase digestion into core particles that contain ∼147 bp of DNA. The 80-bp and 165-bp DNA fragments are incomplete ligation products.