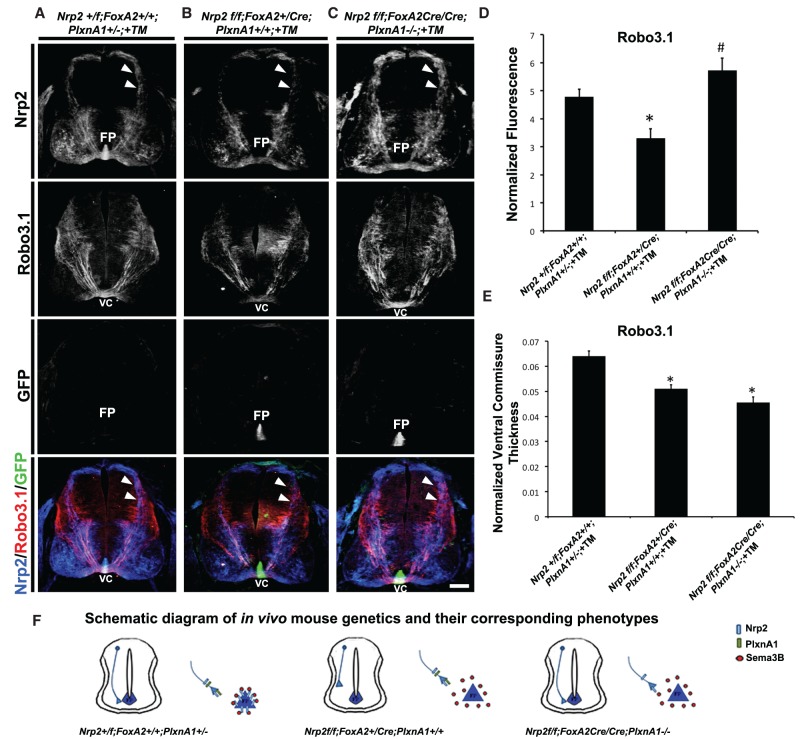
Figure 6.
Precrossing axon guidance defects from floor plate-derived Nrp2-deficient animals are rescued by inhibition of PlxnA1 signaling in vivo. (A–C) Representative confocal images of E11.5 spinal cord sections taken from littermates treated with TM (+TM) with the following genotypes: Nrp2f/f;FoxA2+/+;PlxnA1+/− (A), Nrp2f/f;FoxA2+/CreERT2;PlxnA1+/+ (B), and Nrp2f/f;FoxA2CreERT2/CreERT2;PlxnA1−/− (C). All transverse sections were processed for immunocytochemistry for Nrp2 (blue), Robo3.1 (red), and GFP (green). White arrowheads illustrate Nrp2-positive dorsal commissural axons projecting toward the floor plate (FP) and ventral commissure (VC) in Nrp2f/f;FoxA2+/+;PlxnA1+/− (control) and Nrp2f/f; FoxA2CreERT2/CreERT2;PlxnA1−/− (rescued) embryos but missing in Nrp2f/f; FoxA2+/CreERT2;PlxnA1+/+ animals. Bar, A–C, 125 µm. (D) Quantifications of Robo3.1-normalized fluorescence in Nrp2+/f;FoxA2+/+;PlxnA1+/− +TM, Nrp2f/f;FoxA2+/CreERT2;PlxnA1+/+ +TM, and Nrp2f/f;FoxA2CreERT2/CreERT2;PlxnA1−/− +TM littermate embryos. Data are means ± SEM from five to eight sections per embryo, where n = 3 embryos per genotype combination analyzed. ANOVA followed by post-hoc Tukey test, (*) P < 0.05 compared with Nrp2+/f;FoxA2+/+;PlxnA1+/− +TM; (#) P < 0.05 compared with Nrp2f/f;FoxA2+/CreERT2;PlxnA1+/+ +TM; no significant difference for comparison between Nrp2+/f;FoxA2+/+;PlxnA1+/− +TM and Nrp2f/f;FoxA2CreERT2/CreERT2;PlxnA1−/− +TM. (E) Quantifications of normalized ventral commissure thickness in Robo3.1-positive axons in Nrp2+/f;FoxA2+/+;PlxnA1+/− +TM, Nrp2f/f;FoxA2+/CreERT2;PlxnA1+/+ +TM, and Nrp2f/f;FoxA2CreERT2/CreERT2;PlxnA1−/− +TM littermates. Data are means ± SEM from five to eight sections per embryo, where n = 3 embryos per genotype combination analyzed. ANOVA followed by post-hoc Tukey test, (*) P < 0.05 compared with Nrp2+/f;FoxA2+/+;PlxnA1+/− +TM. (F) Schematic diagram of in vivo mouse genetics and the corresponding phenotypes observed.