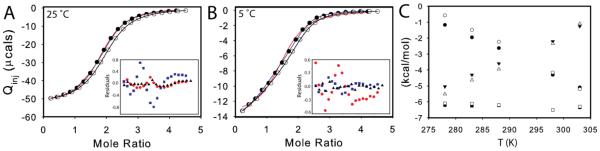
Figure 1.
ITC measurement of dUMP binding to TSase. Conditions are 290 uM TSase in the cell and 6 mM dUMP in the syringe, both in 25 mM NaPO4, 1 mM EDTA, and 2 mM TCEP, pH 7.5. (A, B) Fits are shown for dUMP titrations using models for one-site binding (red line against closed circles), general two-site binding (blue line against closed circles), and modified general binding (black lines against open circles); insets show residuals for one-site binding (red circles), general two-site binding (blue squares), and modified general binding (black triangles). For both 25 °C (A) and 5 °C (B), original data points are shown as filled circles, and data points corrected for cell concentration are shown as open circles. C) The modified general model was used to fit ITC data at multiple temperatures. The thermodynamic parameters, ΔH (circles), -TΔS (triangles) and ΔG (squares), for binding to free (black) and singly bound (white) TSase are shown as functions of temperature. The slope of ΔH versus T yields ΔCp=-157 cal/molK and ΔCp=-183 cal/molK for binding to free and singly bound TSase, respectively. Errors in parameters were determined from Monte Carlo simulations and the error bars are smaller than the points. Values for fitted parameters from the modified general model are shown in Table S2.