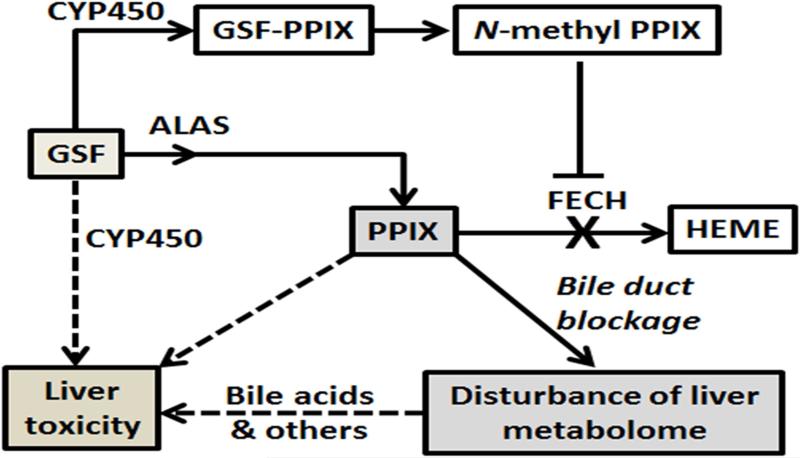
Figure 7. Proposed mechanisms of GSF-induced liver injury in mice.
CYP450-mediated GSF bioactivation leads to the formation of N-methyl PPIX, which inhibits the FECH-mediated conversion of PPIX to heme. Together with GSF-mediated induction of ALAS [9], the rate liming enzyme in heme synthesis, GSF treatment results in a significant accumulation of PPIX in the liver. PPIX and other endobiotics that are stuck in the liver because of PPIX-mediated bile duct blockage contribute to GSF-induced liver injury. Reactive metabolites generated by CYP450-mediated GSF bioactivation may also contribute to hepatotoxicity of GSF.