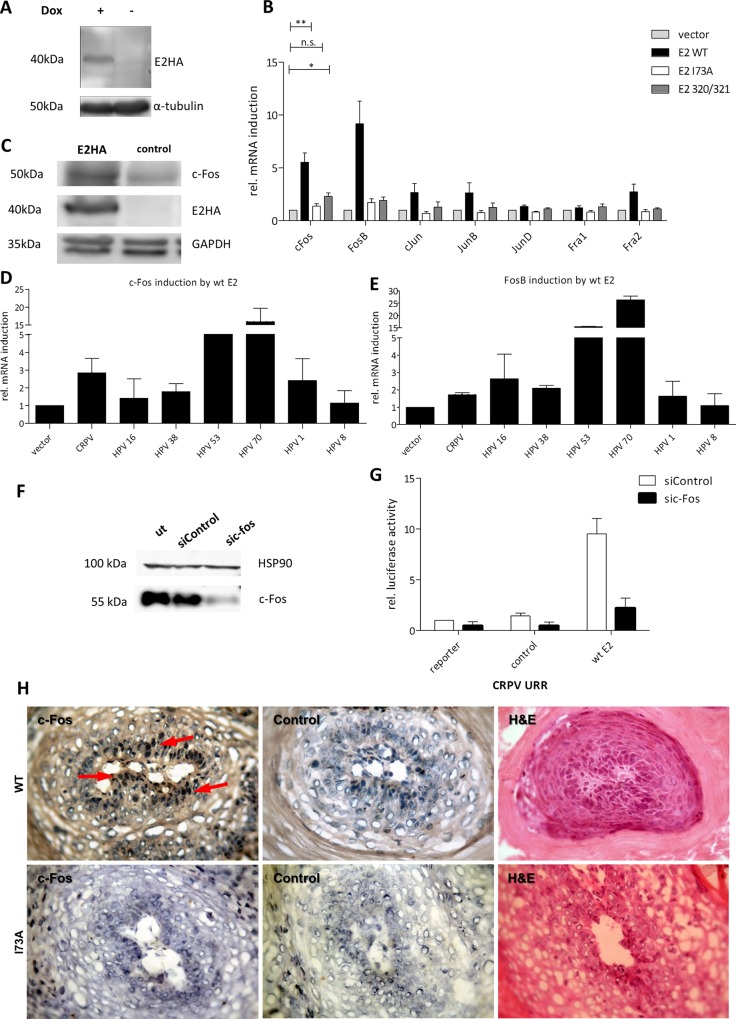
Fig 4. The cellular gene c-Fos inducible by E2 is a component of the AP1 complex driving the viral promoter.
(A) Western blot of the inducible C33A cell line for detection of HA-tagged E2 48h after addition of doxycycline (+). Alpha-tubulin was used as a loading control. (B) C33A cells were transfected with empty vector (control) and either wt E2, E2-I73A or K320M/C321R (E2 320/321). 48 h later the cells were harvested and analyzed for AP1-monomers mRNA induction. Unpaired two tailed t test was used for statistical significance (*p<0.05, **p<0.01). (C) Western blot analysis of E2 and c-Fos expression compared to the empty vector (control). C33A cells were transfected as before and treated with 10 μM lactacystin 6h before harvest to prevent protein degradation. GAPDH was used as a loading control. (D) c-Fos and (E) FosB mRNA induction by E2 proteins from different PVs. C33A cells were transfected as before and analyzed for c-Fos and FosB mRNA induction compared to the control (empty vector). (F) Western blot of C33A cells that were transfected with a pool of three c-Fos siRNAs (sic-Fos) and a control siRNA (siControl). 10 μM of MG-132 was added to the medium 6h before harvest. HSP90 was used as a loading control. (G) Activation of the wt CRPV-URR by wt E2 after c-Fos silencing. The values are related to the basal activity of the CRPV-URR reporter co-transfected with empty vector and the siControl. (H) Immunohistochemistry of I73A and wt CRPV induced papillomas using an antibody against c-Fos. Control: Incubation with secondary antibody only. The arrow indicates nuclear c-Fos staining.