Fig 7. Model of the molecular actions of NO-cGMP signaling and HU.
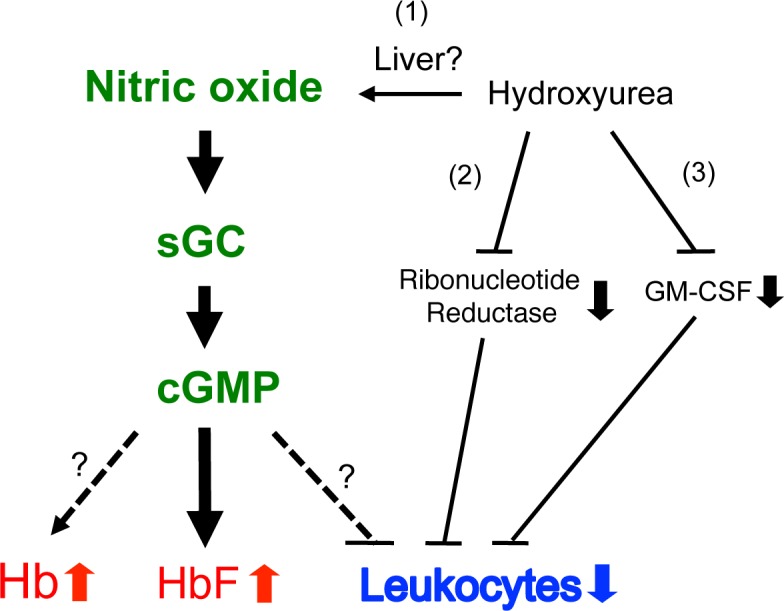
While the current study has shown hematologic effects of NO-cGMP signaling on RBCs and leukocytes, the molecular actions of HU are yet to be elucidated. NO may be generated when HU is metabolized in the liver (pathway 1). HU may reduce leukocyte counts by inhibiting DNA synthesis through ribonucleotide reductase (pathway 2) [58] or GM-CSF (pathway 3) [56]. cGMP induces HbF expression [21] and inhibition of ribonucleotide reductase may account in part for leukocyte reduction and HbF induction [61]. This study suggests that cGMP may also be associated with a rise in total hemoglobin (Hb) and a decrease in leukocyte count. Solid lines represent molecular actions noted in the literature and dotted lines indicate those examined in this study.
