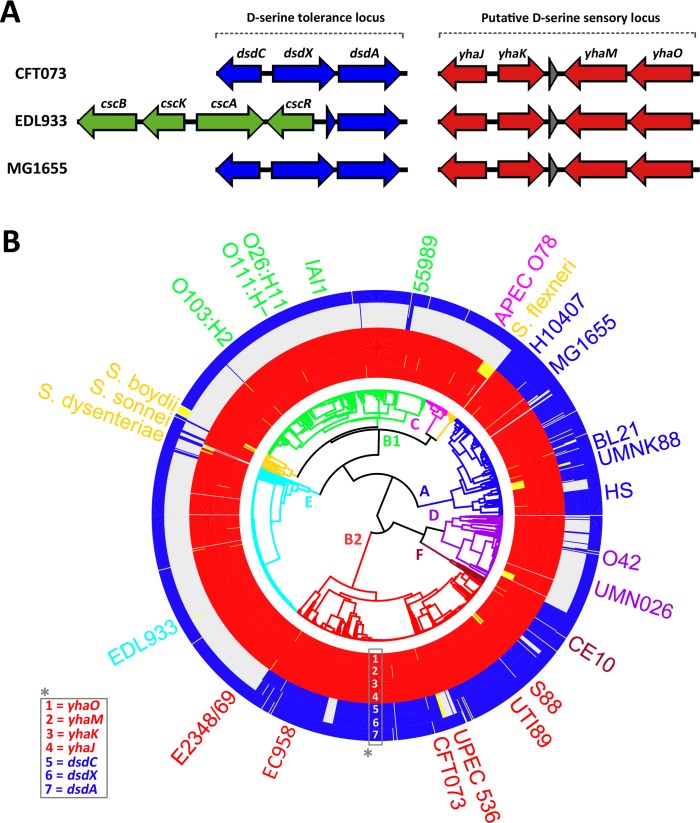
Fig 1. Genomic and phylogenomic context of the yhaOMKJ locus.
(A) Genomic context of the D-serine tolerance locus (blue) in three distinct E. coli isolates–CFT073 (UPEC), EDL933 (EHEC) and MG1655 (K-12). The system encodes DsdC (a LysR type transcriptional regulator), DsdX (a D-serine outer membrane transporter) and DsdA (a D-serine deaminase). In EDL933 the D-serine tolerance locus is truncated and replaced with the sucrose utilization locus (cscRAKB highlighted in green). (B) Genomic context of the second putative D-serine sensory locus (red) in CFT073, EDL933 and MG1655. The system encodes YhaJ (a putative LysR type transcriptional regulator), YhaK (a redox-sensitive bicupin), YhaM (a putative deaminase) and YhaO (a putative inner membrane D-serine transporter). (B) The yhaOMKJ locus is highly conserved across the E. coli phylogeny. Circularized phylogenomic tree of 1591 E. coli and Shigella isolates overlaid with gene carriage for the dsdCXA locus and the yhaOMKJ locus. The yhaOMKJ genes are indicated by red blocks and the dsdCXA locus by blue blocks. Ordering of the genes is numbered and corresponds to the gene in the legend labeled *. Presence of a gene is determined by > 80% identity over > 80% of the coding sequence. Pseudogenes are indicated as yellow blocks. E. coli phylogroups are subdivided by color with the branch point labeled on the tree. Phylogroup A = Blue; Phylogroup B1 = Green; Phylogroup B2 = Red; Phylogroup C = Magenta; Phylogroup D = Purple; Phylogroup E = Cyan; Phylogroup F = Brown; Shigella = Gold. The position of prototypical strains is indicated on the outside of the figure.