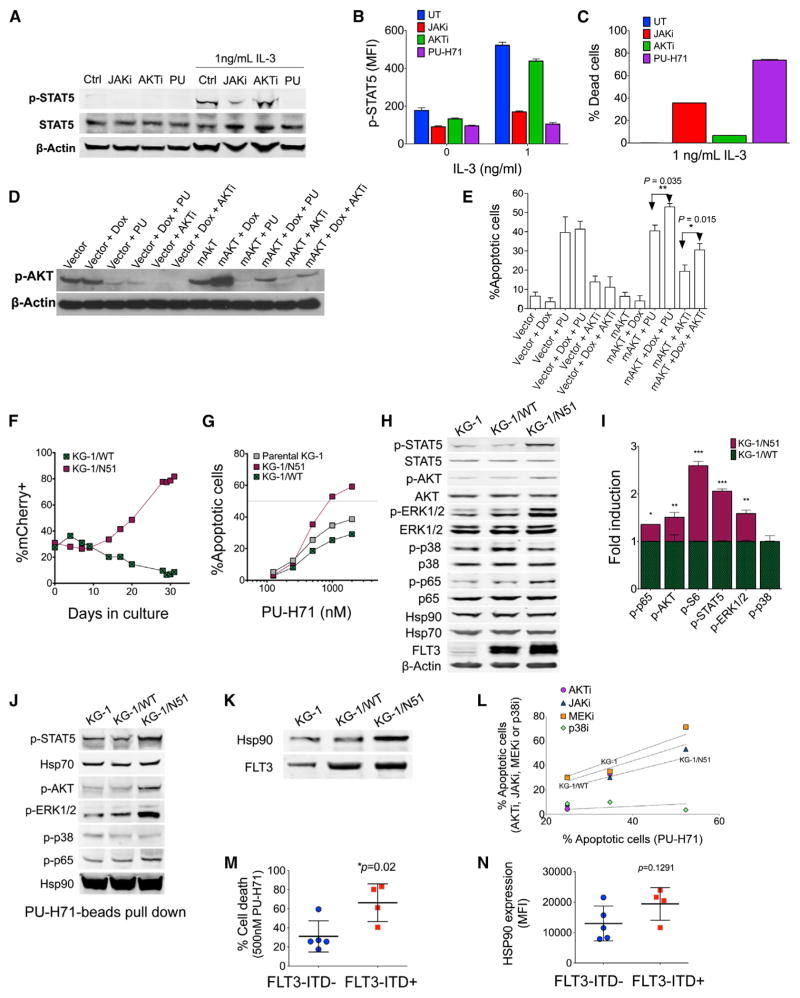
Figure 4. Activation of JAK, AKT, and ERK Pathways Renders AML Cells Addicted to teHsp90.
(A and B) Immunoblot (A) and flow cytometry (B) of FL5.12 cells after 24 hr treatment with JAKi, AKTi, or PU-H71 (PU) in the presence or absence of IL-3.
(C) Percent dead cells in FL5.12 cells after 48 hr treatment with JAKi, AKTi, or PU.
(D and E) Immunoblots for pAKT (D) and percent apoptotic cells (E) of vector control- or mAKT-transfected cells treated with PU-H71, AKTi ± doxycycline (DOX) for 24 hr or 48 hr, respectively.
(F) Percentage of mCherry+ cells KG-1/N51 or KG-1/WT over 30-day cultures.
(G) Percentage of apoptotic cells after 48 hr treatment with PU-H71.
(H and I) Phosphorylated protein levels in cells evaluated by immunoblot (H) or flow cytometry (I) (fold change of MFI for KG-1/N51 relative to KG-1/WT).
(J) Immunoblots of Hsp90-interacting proteins as isolated by PU-beads.
(K) Immunoblots for Hsp90 and FLT3 immunoprecipitated with an anti-FLT3 antibody.
(L) Correlation of the apoptotic sensitivity to PU-H71 (x axis) and to AKTi, JAKi, MEK1/2i, or p38i (y axis) in cells treated for 48 hr.
(M) Percent cell death for FLT3-ITD− or FLT3-ITD+ primary AML cells after 48 hr exposure to PU-H71.
(N) Hsp90 expression of cells from (M) as measured by flow cytometry. Each symbol represents an individual sample.
Values denote mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01;***p < 0.001. See also Figure S4.