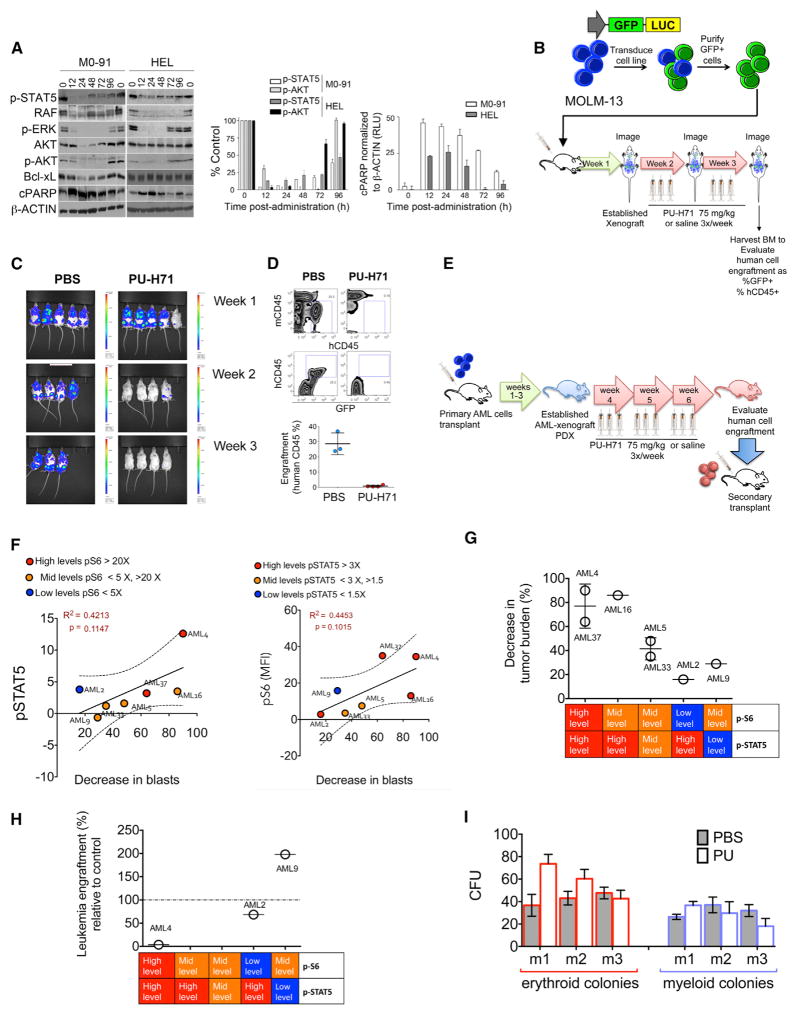
Figure 6. PU-H71 Ablates In Vivo LSCs of Primary AML Samples with High pSTAT5 Levels.
(A) Immunoblots (left) and graphed summary (right; means ± SEM) for the indicated proteins in M0-91 or HEL cells-engrafted mice after one dose of PU-H71 (75 mg/kg).
(B) Schematic representation for the in vivo treatment of MOLM-13-GFP-Luc xenografts.
(C) Whole-body luciferase imaging of MOLM-13-GFP-Luc xenografts before and during treatment with PU-H71.
(D) Top panel: representative plots for mouse (mCD45) and human (hCD45) BM cells harvested from MOLM-13-GFP-Luc xenografts after 2 weeks of treatment with PU-H71. Bottom panel: percent human cells in xenografts treated with either PBS or PU-H71 (PU) is shown.
(E) Schematic representation for the in vivo AML-patient-derived xenograft (PDX) treatments.
(F) Correlations between p-STAT5 (y axis; left panel) and pS6 (y axis; right panel) and decreased tumor burden after PU-H71 treatment (x axis).
(G) Percent decrease in tumor burden after treatment with PU-H71 for seven PDX-AML xenograft cohorts grouped by their relative levels of pSTAT5 and pS6.
(H) Percent leukemia engraftment in secondary transplants for the indicated PDX-AML xenograft cohorts grouped by their relative levels of pSTAT5 and pS6.
(I) CFUs of murine bone marrow cells evaluated from disease-free C57BL6 mice treated for 3 weeks with either PBS or PU-H71.