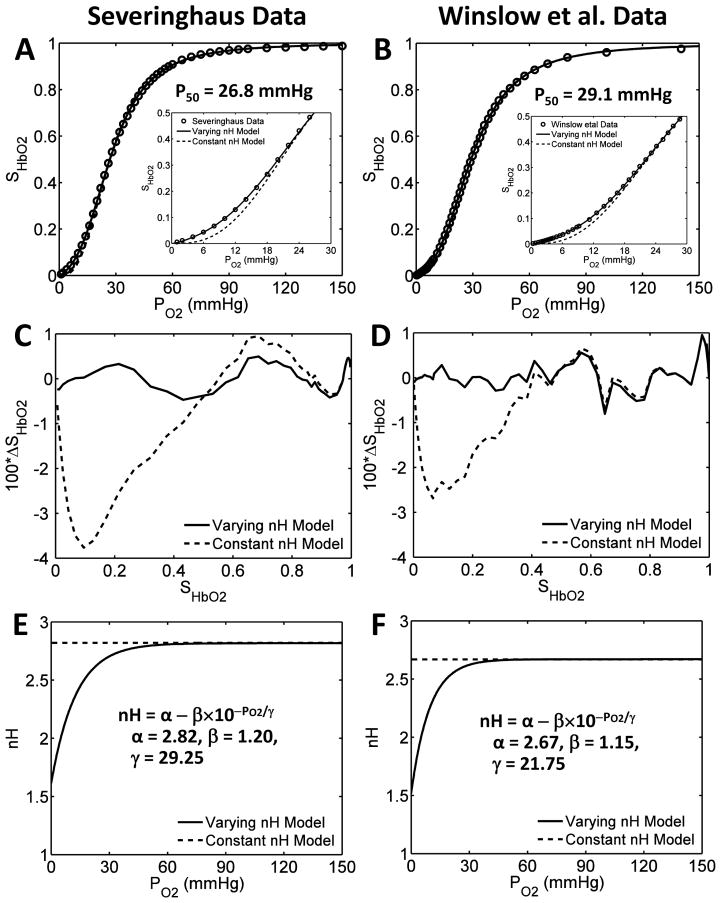
Figure 1. Illustration of the accuracy of the modified SHbO2 model under standard physiological conditions with PO2-dependent variable cooperativity hypothesis for O2-Hb binding.
(A,B) Comparison of the model-simulated HbO2 dissociation curves with constant and variable cooperativity hypotheses for O2-Hb binding (constant and variable Hill coefficient nH) to available experimental data in the literature, on normal human blood at standard physiological conditions. The simulations in panel A are compared to the data of Severinghaus and colleagues (Roughton et al., 1972; Roughton & Severinghaus, 1973; Severinghaus, 1979), and those in panel B are compared to the data of Winslow et al. (1977). The simulations in the main plots are compared to the data over the whole SHbO2 range, while those in the inset plots are compared to the data for SHbO2 ≤ 0.5, effectively demonstrating the improved accuracy of the modified SHbO2 model with variable nH in simulating the data in the lower SHbO2 range. (C,D) The percentage deviations (100 × ΔSHbO2) of the model-simulated SHbO2 values from the experimental SHbO2 values for the constant and variable nH models plotted as functions of SHbO2 for the data of Severinghaus and colleagues (Roughton et al., 1972; Roughton & Severinghaus, 1973; Severinghaus, 1979) and Winslow et al. (1977). The incorporation of the variable cooperativity hypothesis for O2-Hb binding (variable nH) has improved the accuracy of the SHbO2 model. (E,F) The PO2-dependent variation of nH corresponding to the constant and variable cooperativity hypotheses for O2-Hb binding that are obtained based on fittings of the modified SHbO2 model to the data of Severinghaus and colleagues (Roughton et al., 1972; Roughton & Severinghaus, 1973; Severinghaus, 1979) and Winslow et al. (1977). The insets in plots (E,F) show the expressions for the variable nH and the governing parameter values for the two data sets.