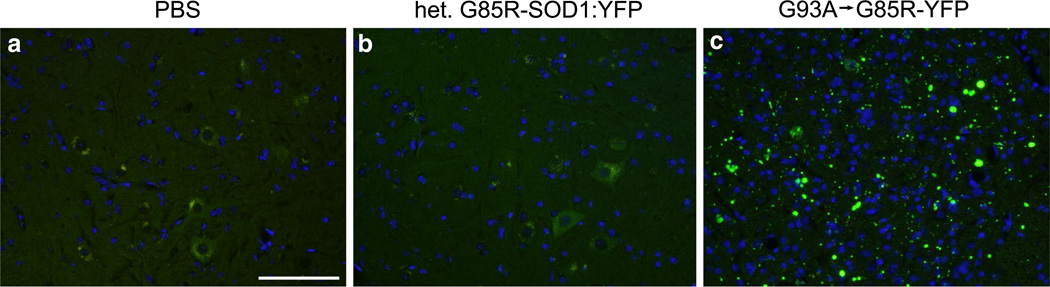
Fig. 2.
Induction of inclusion pathology in G85R-SOD1:YFP mice injected with G93A → G85R-SOD1:YFP spinal cord homogenate. G85R-SOD1:YFP mice were injected unilaterally in their sciatic nerve with either PBS (a), homogenate from an asymptomatic heterozygous G85R-SOD1:YFP mouse (b), or homogenate from a mouse paralyzed by injection of G93A → G85R-SOD1:YFP second passage homogenates (c). The PBS-injected mice (n = 3) were harvested at 12.6 months p.i. and mice injected with homogenate from the asymptomatic G85R-SOD1:YFP mouse (n = 5) were harvested at 8.5 months p.i.; neither cohort displayed G85R-SOD1:YFP inclusion pathology in any level of their spinal cord. Abundant YFP inclusion pathology was observed in end-stage mice (~3 months) injected with the second passage G93A → G85R-SOD1:YFP homogenates (n = 8). Scale bars 100 µm