Fig 1. Structure of cranberry-derived flavonoids for combination therapy.
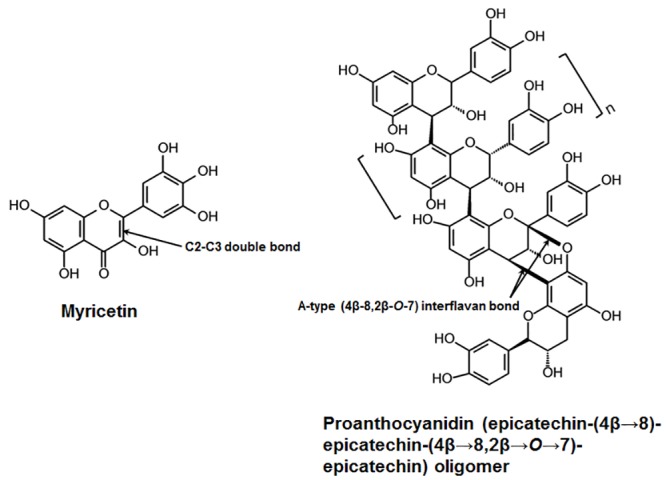
Myricetin, one of the most active cranberry flavonols, is characterized by the presence of an unsaturated double bond between C2 and C3 and three hydroxyl-groups in the B ring. Proanthocyanidins (PACs) in cranberry are predominantly found in oligomeric forms (up to 13 monomeric units) with at least one A-type double interflavan linkage [epicatechin-(4β→8, 2β→O→7)-epicatechin] between the lower or lowest two units of the oligomer. The degree-of-polymerization (DP) is variable depending on the number of monomeric units; DP4 (tetramer) and DP9 (nonamer) are among the most abundant and bioactive cranberry PAC.
