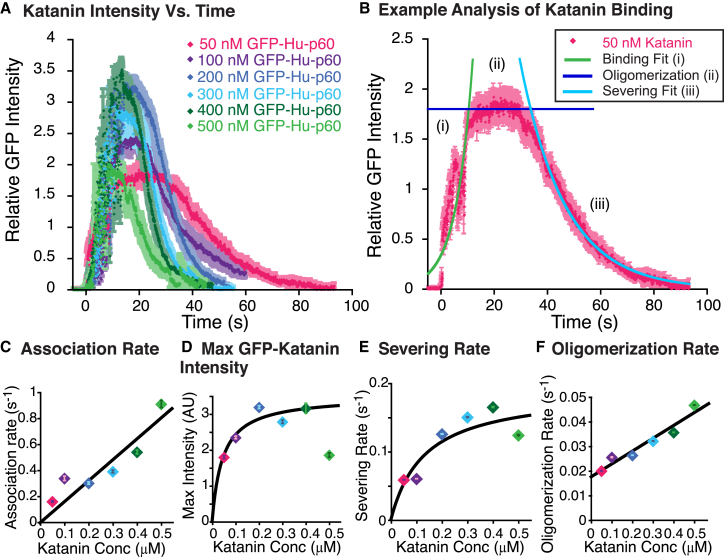
Figure 2.
Fast katanin severing activities are concentration dependent. (A) Data of GFP-Hu-p60 binding and severing taken at 25.6 frames/s plotted over time after translating the data so that the binding occurs at t = 0 s. GFP-Hu-p60 concentrations were 50 nM (pink diamonds, N = 13), 100 nM (purple diamonds, N = 51), 200 nM (dark blue diamonds, N = 48), 300 nM (light blue diamonds, N = 53), 400 nM (dark green diamonds, N = 25), and 500 nM (light green diamonds, N = 11). Error bars (shown in paler versions of the marker colors) represent mean ± SE. (B) Example data set for 50 nM GFP-Hu-p60 shows the data (pink diamonds) has three distinct phases: (i) the exponential growth phase of GFP-Hu-p60 binding fit with Eq. 4 (green line), (ii) the pre-severing phase of oligomerization estimated as the average value (dark blue line), and (iii) the exponential decay phase where the katanin severs the microtubule fit with Eq. 5 (light blue line). (C) Characteristic binding rate from the fits to the initial binding phase plotted against katanin concentration. Error bars denote the uncertainty of the fit parameter. Data are fit to Eq. 6. (D) Plot of the maximum GFP intensity when GFP-Hu-p60 was bound in the pre-severing phase. Error bars represent mean ± SE. Data are fit to Eq. 7. (E) Plot of the characteristic severing rate from the fit to the severing phase plotted against the added katanin concentration. Error bars denote the uncertainty of the fit parameter. Data are fit to Eq. 8. (F) Plot of the oligomerization rate characterized by the pre-severing phase as a function of the added GFP-Hu-p60 concentration. Error bars represent propagated uncertainty from fit parameters τbind and t0. Data are fit to Eq. 9. Fit parameters for all data sets can be found in Table S2. For (C)–(F), error bars are represented in front of the marker, but most were smaller than the marker size.