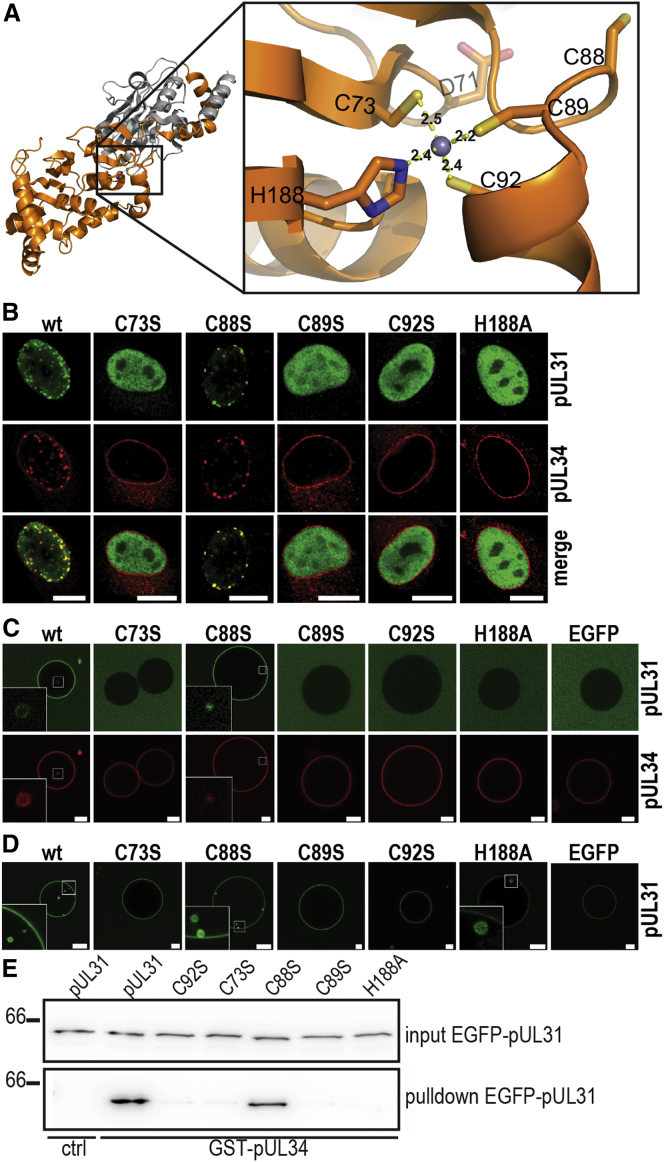
Figure 2.
pUL31 ZNF Motif Is Vital for NEC Function
(A) Close-up view on the pUL31 ZNF motif. The side chains Cys73, Cys89, Cys92, and His188 coordinating the Zn2+ ion are shown as sticks, and respective distances (in angstroms) are indicated. Colors are as described in Figure 1A.
(B) In situ phenotype of pUL31 mutants. RK13 cells were co-transfected with WT pUL34 and pUL31 WT or mutant constructs. Proteins were detected by immunofluorescence with respective antibodies followed by confocal microscopy of the nuclear region. Anti-pUL31 is shown in green; anti-pUL34 is shown in red. Scale bars, 10 μm.
(C and D) In vitro phenotype of mutations in the ZNF motif affecting vesicle formation. (C) Soluble WT pUL31 (expressed as an EGFP fusion) was added to pUL34-GUVs. Recruitment of pUL31 and vesicle formation into the GUV lumen was assayed. Green channel shows pUL31-EGFP; red channel shows Alexa Fluor 546-labeled pUL34. (D) His6-tagged-EGFP or His6-tagged-EGFP-pUL31 proteins were directly tethered to Ni-NTA-DGS containing GUVs, in the absence of pUL34. Scale bars, 10 μm.
(E) Western blot of pull-downs showing pUL31-pUL34 interactions. Anti-EGFP antibodies were used to detect pull-downs using GST (ctrl) or GST-pUL34 as baits and EGFP-pUL31 WT and mutants as prey (for details, see Experimental Procedures).