Figure 2.
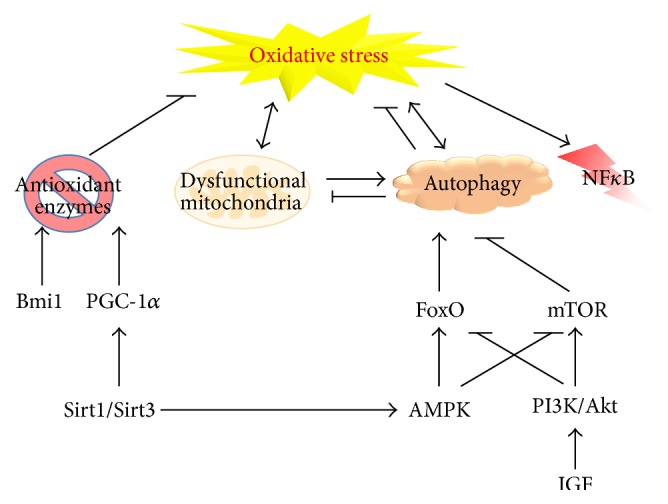
Mechanisms leading to oxidative stress in skeletal muscle. This schematic illustrates cellular mechanisms that are known to exert either prooxidant or antioxidant effects. Aberrant regulation of these pro- and antioxidative processes is indicated to play a role in muscle degenerative disorders. NFκB: nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; Bmi1: B lymphoma Mo-MLV insertion region 1 homolog; PGC-1α: peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1-alpha; FoxO: forkhead box O; mTOR: mechanistic or mammalian target of rapamycin; AMPK: adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase; PI3K: phosphoinositide 3-kinase; IGF: insulin-like growth factor.
