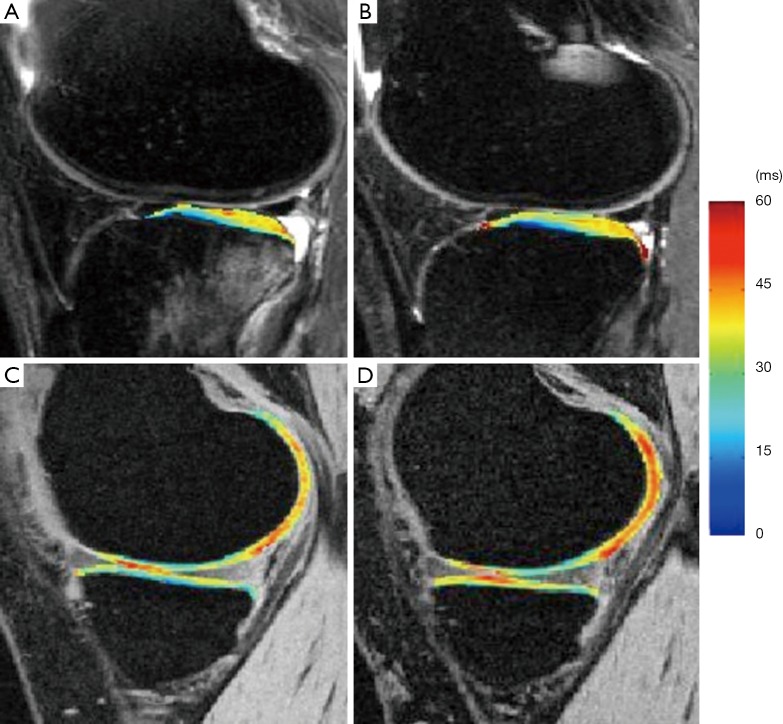
Figure 10.
T1ρ maps of the lateral side (A,B) and medial side (C,D) of an ACL-injured knee at baseline (A,C) and one-year follow up (B,D). T1ρ values in posterior lateral tibia were elevated significantly in ACL-injured knees at baseline and remained high at 1-year follow despite resolution of bone bruise. T1ρ values in the contacting area of medical femoral condyle and medial tibia were significantly elevated in ACL-injured knees at one-year follow up [Reprinted with permission (100)]. ACL, anterior cruciate ligament.