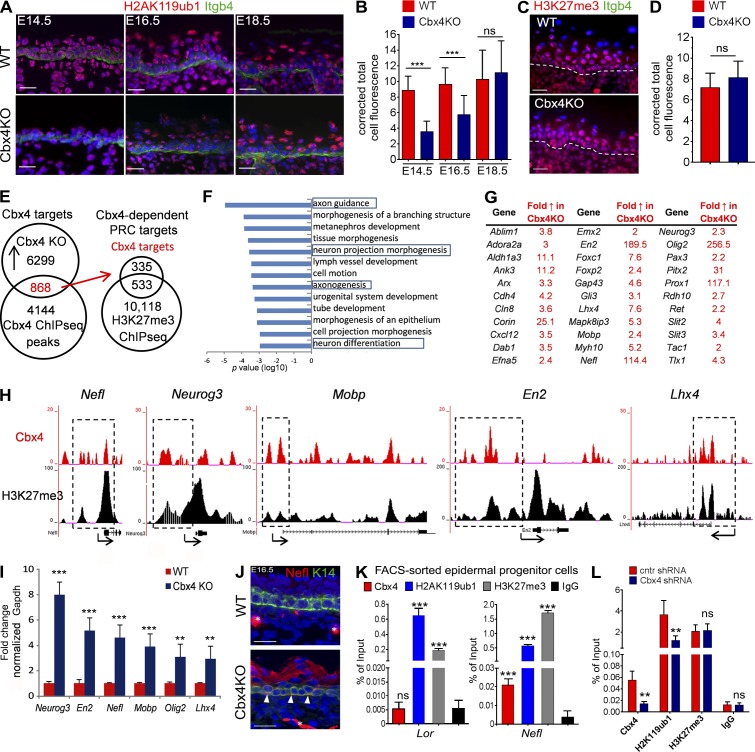
Figure 2.
Activation of nonepidermal lineage genes in Cbx4-deficient epidermis. (A and B) Distribution and quantification of H2AK119ub1 immunofluorescence in WT and Cbx4KO skin. H2AK119ub1 is markedly reduced in the Cbx4KO epidermis at E14.5 and E16.5, whereas its expression is restored by E18.5. (C and D) Lack of changes in the cutaneous H3K27me3 expression between WT and Cbx4KO mice. Dashed lines separate epidermis and dermis. (E) Overlap of the Cbx4 and H3K27me3 ChIP-seq data with the expression arrays obtained from the epidermis of Cbx4KO versus WT mice depicts the direct Polycomb-dependent Cbx4 target genes in KCs that are up-regulated upon Cbx4 ablation. (F) Ontology of the Cbx4 target genes using DAVID bioinformatic resources. The bars represent the log10 p-values of each category. (G) Selected Cbx4 target genes involved in neuronal development and/or functioning. (H) ChIP-seq tracks depicting Cbx4 and H3K27me3 binding to the selected target genes (a single representative experiment out of two repeats is shown). Dashed outlines depict the corresponding gene regulatory regions. (I) qRT-PCR validation of the selected Cbx4 target genes up-regulated in the basal progenitor cells from Cbx4KO mice versus WT controls (mean ± SD). n = 3. (J) Ectopic Nefl protein expression in the Cbx4KO epidermis (arrowheads) compared with WT counterparts. Asterisks denote Nefl+ dermal nerve fibers in the WT and Cbx4KO mice. (K) ChIP-qPCR shows Cbx4 binding to Nefl but not to Lor promoter regions. Both Lor and Nefl are enriched in H2AK119ub1 and H3K27me3 histone marks (mean ± SD). n = 3. (L) Cbx4 knockdown in primary mouse KCs with shRNA decreases Cbx4 binding and reduces the H2AK119ub1 enrichment on the Nefl promoter region (mean ± SD). n = 3. **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001. Bars, 25 µm. ns, not significant.