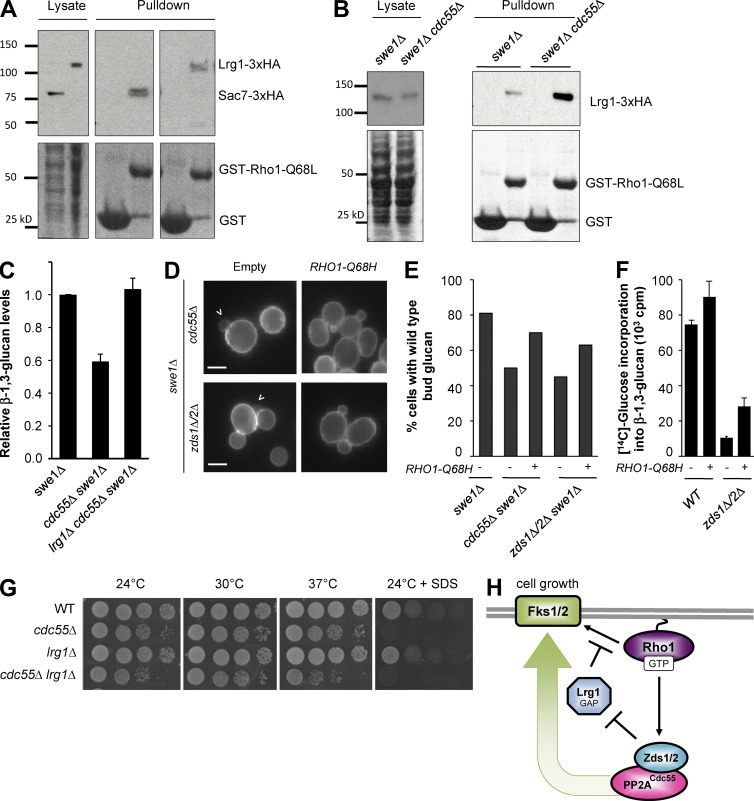
Figure 3.
A Rho1–Zds1/Zds2–PP2ACdc55 positive feedback loop promotes glucan synthesis by inhibition of Lrg1. (A) Pull-down assay for monitoring active Rho1 GAP. GST-Rho1Q68L was incubated with yeast cell lysates expressing 3XHA-tagged Sac7 or Lrg1. Lysates and bead-bound fractions were subjected to SDS-PAGE and Western blotting with anti-HA antibody. (B) In cdc55Δ, more Lrg1-3XHA bound to GST-Rho1Q68L beads compared with wild-type (WT) lysates. (C) Deletion of LRG1 rescued the glucan synthesis defect of cdc55Δ cells. Normalized total glucan synthesis as assayed in Fig. 2 E for indicated strains. (D) Activation of Rho1 can bypass Zds1/Zds2–PP2ACdc55 regulation of glucan synthesis. Arrowhead denotes cells with reduced glucan staining. (E) Quantification of small budded cells with wild-type glucan staining in the bud from D. (F) β-1,3-glucan synthesis defect of zds1Δ zds2Δ is partially rescued by RHO1-Q68H. (G) Deletion of LRG1 did not rescue the SDS sensitivity of cdc55Δ cells. Serial dilutions of yeast strains spotted on YPD with or without 0.03% SDS plates at the indicated temperature. (H) Model for how Zds1/Zds2–PP2ACdc55 promotes glucan synthesis through the inhibition of Rho1 GAP Lrg1.