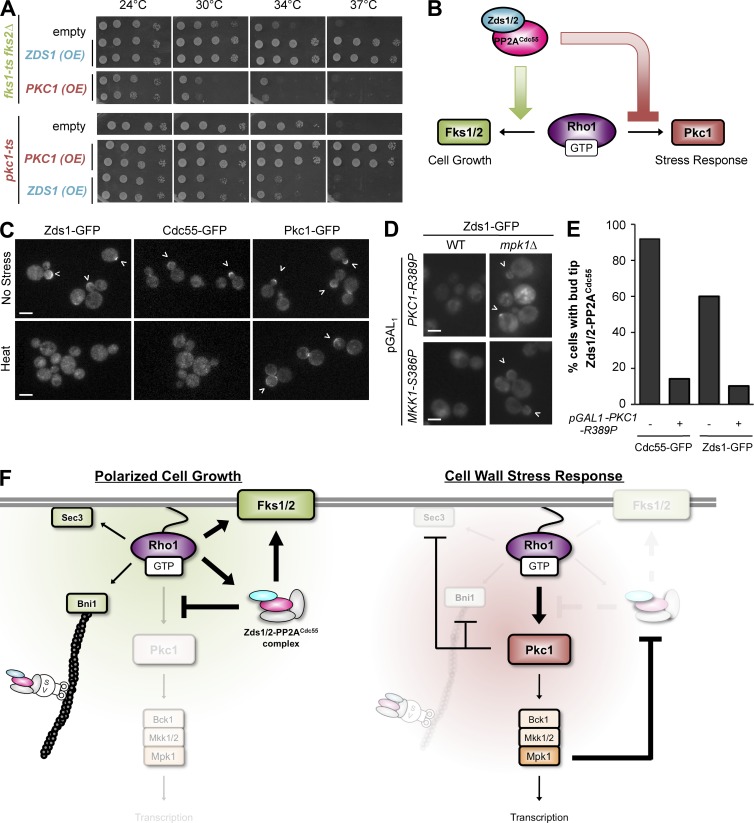
Figure 5.
Mutual antagonism between Zds1/Zds2–PP2ACdc55 and Pkc1 controls Rho1 activation of polarized cell growth or stress response. (A) Overexpression of ZDS1 rescued glucan synthase mutant fks1-ts fks2Δ but inhibited growth of pkc1-ts mutant at higher temperature. (B) Working model for Zds1/Zds2–PP2ACdc55 function. Zds1/Zds2–PP2ACdc55 promotes Rho1–Fks1/Fks2 glucan synthesis while inhibiting the Rho1–Pkc1 stress pathway. (C) Cell wall stress removes Zds1/Zds2–PP2ACdc55 complex from the bud cortex. Zds1-GFP and Cdc55-GFP but not Pkc1 are delocalized from the bud cortex (arrowheads) after a heat shock at 39°C. (D) Artificial activation of Pkc1 or Mkk1 is sufficient to remove Zds1 from the cortex in a MPK1-dependent manner. WT, wild type. (E) Quantification of cells with cortically localized Cdc55-GFP or Zds1-GFP before (−) and after (+) GAL induction of the activated PKC1-R389P mutant. More than 50 cells were counted for each strain and condition. (F) Model for the Zds1/Zds2–PP2ACdc55 complex regulation of Rho1 signaling during polarized cell growth (left) and cell wall stress response (right). Two mutually exclusive Rho1 signaling states are maintained by an antagonism between the Zds1/Zds2–PP2ACdc55 complex and Pkc1 kinase.