Figure 1.
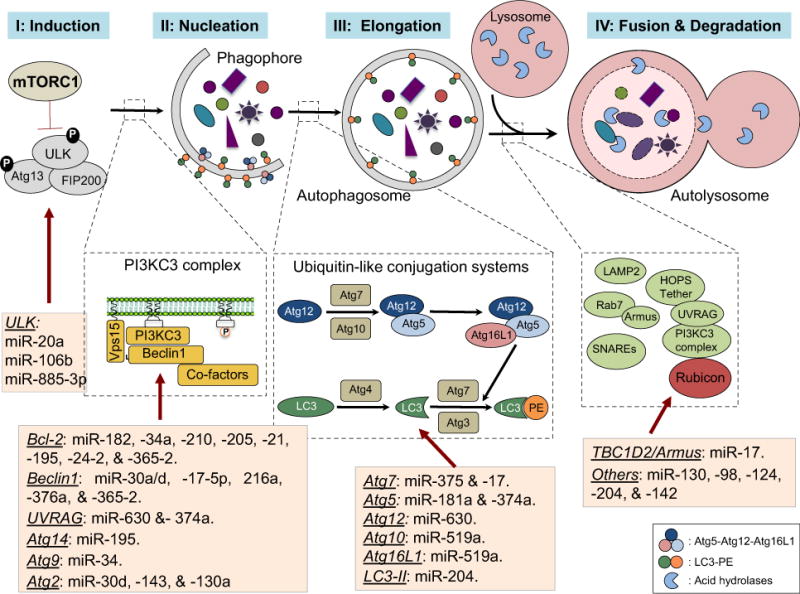
Schematic representation of the core autophagy pathway and its regulation by miRNAs. Autophagy proceeds through a series of steps including induction, vesicle nucleation, membrane elongation, and autophagosome maturation into the lysosome for degradation and recycling. miRNAs regulation occurs at each dynamic step. Autophagy induction is directly and tightly controlled by the ‘nutrient sensor’ mTORC1, which under nutrient-rich condition precludes the assembly and the activation of the autophagy-initiating ULK complex comprising ULK1/2, Atg13, and FIP200 (Step 1). mTORC1 is inactivated in response to various stimuli (for instance, starvation, hypoxia), which enables the activation of the ULK complex and triggers the autophagy cascade. MiR-20a, miR106b, and miR-885-3P target ULK1/2 and suppress autophagy. Phagophore nucleation, which is confined to the phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate (PI3P)-containing vesicles, is driven by the Beclin1-associated PI3KC3 complex (Step 2). The activity of this kinase complex is suppressed by the anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 proteins, a functional target of multiple miRNAs such as miR-182, miR-34a, miR-210, miR-205, miR-21, miR-195, miR-24-2, and miR-365-2. Beclin1 can also be targeted by miR-30a, miR-30d, miR-17-5p, miR-216a, miR-376a, and miR-365-2. In addition, UVRAG is a direct and functional target of miR-630 and miR-374a, while Atg14 being inhibited by miR-195. Autophagosome membrane elongation involves two ubiquitin-like conjugation systems: one is Atg12-Atg5 conjugation and the other is LC3-phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) conjugation, the latter of which is sequentially processed by Atg4, Atg7, and Atg3 (Step 3). Atg7 can be suppressed by miR-375 and miR-17. LC3-II levels are posttranscriptionally controlled by miR-204. Fusion of the autophagosome with the lysosome signifies the maturation stage of the autophagy pathway, a step that involves multiple membrane fusion factors and is negatively regulated by the Rubicon complex (Rubicon-UVRAG-Beclin1-PI3KC3-p150). Finally, the encapsulated contents, together with the inner membrane of the autophagosome, undergo breakdown by lysosomal hydrolases.
