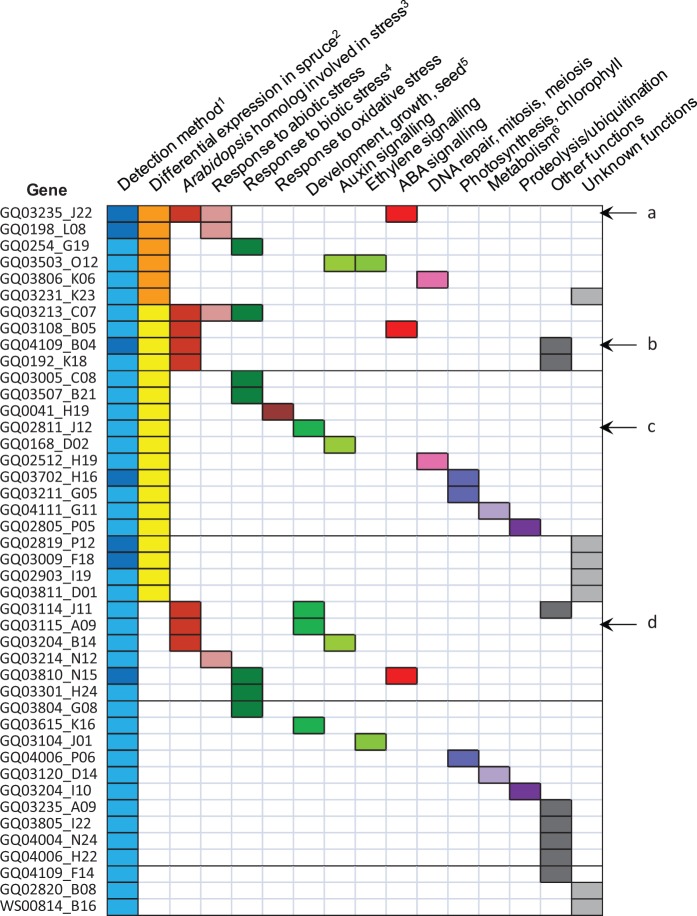
Fig. 6.—
Functional classification of the 43 Picea glauca genes carrying highly significant SNPs associated with climate. Each line corresponds to one of the 43 adaptive genes. The categorization into functional classes was determined after transcriptome analyses and literature search about the functions of homologs (see Materials and Methods, Supplementary Table S3A). 1Adaptive genes detected by regression (FDR = 0.05) or Random Forest (top 10) alone (pale blue), or by both methods (dark blue). 2Adaptive genes differentially expressed (or matching a Picea sitchensis DEG) during bud set in P. glauca or P. sitchensis alone (yellow), or in both species (orange). The experiments were published by El Kayal et al. (2011) and Galindo-Gonzalez et al. (2012) for P. glauca, and by Holliday et al. (2008) for P. sitchensis. 3Picea glauca adaptive genes matching an Arabidopsis gene transcriptionally regulated by cold and/or drought and/or salt and/or UV-B stresses (Kilian et al. 2007). 4Genes with homologs involved in defense mechanisms against several pathogens (e.g., bacteria, nematodes, herbivory). 5Genes involved in development, growth, or seed development. 6Genes involved in secondary metabolism, lignin accumulation. Letters and arrows on the right indicate the main genes discussed in the text. (a) CIPK20, (b) β-tubulin, (c) PP2A catalytic subunit, (d) PP2A regulatory subunit.