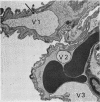
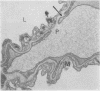
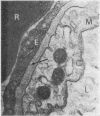
Abstract
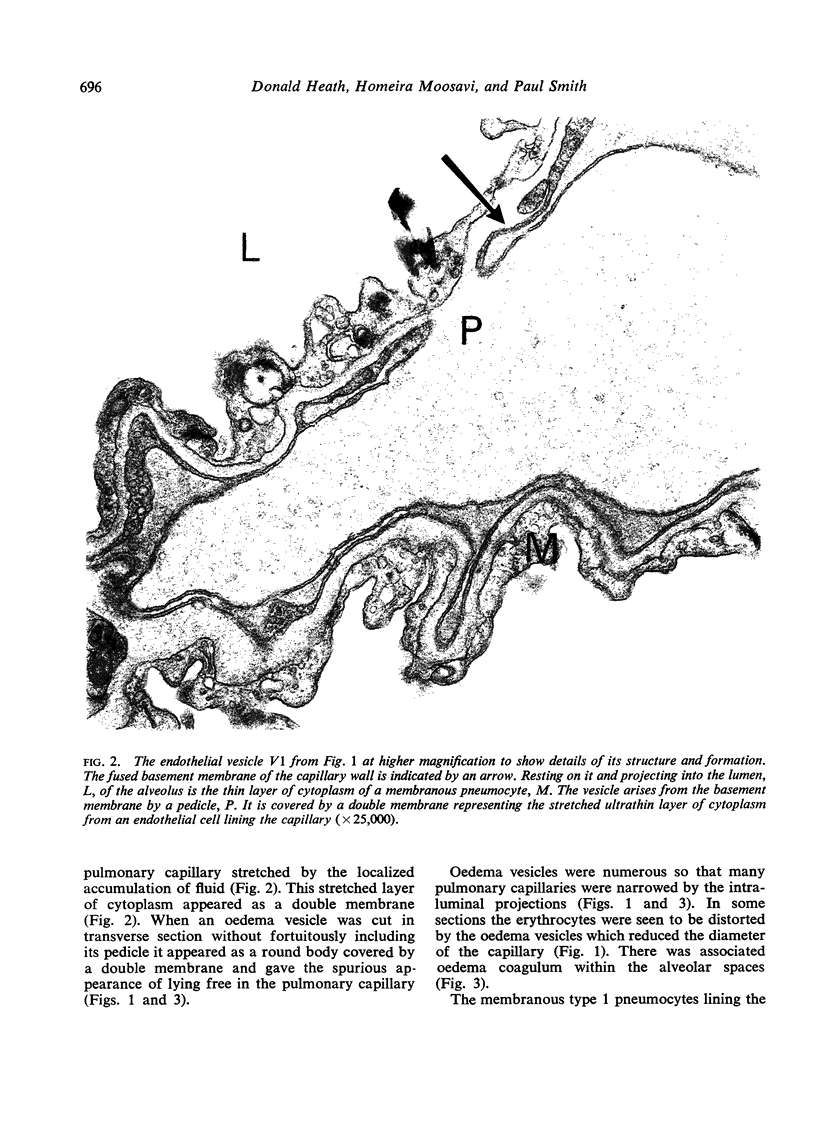
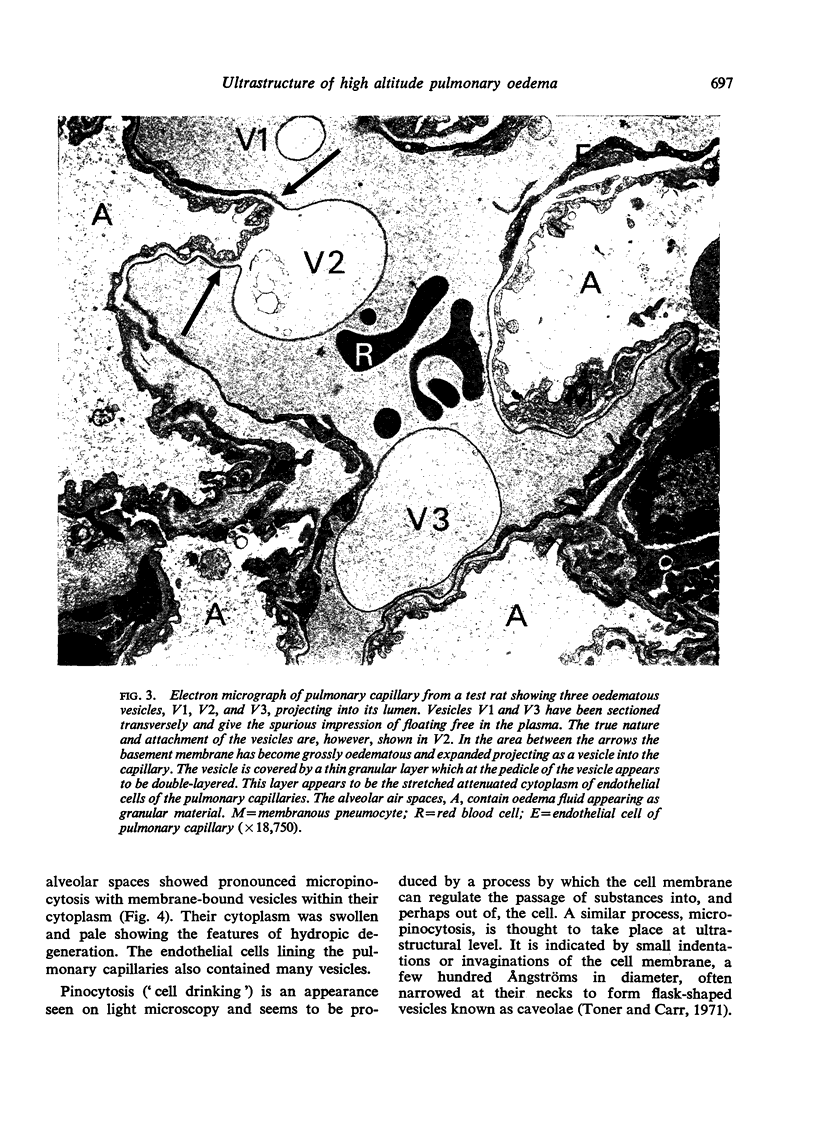
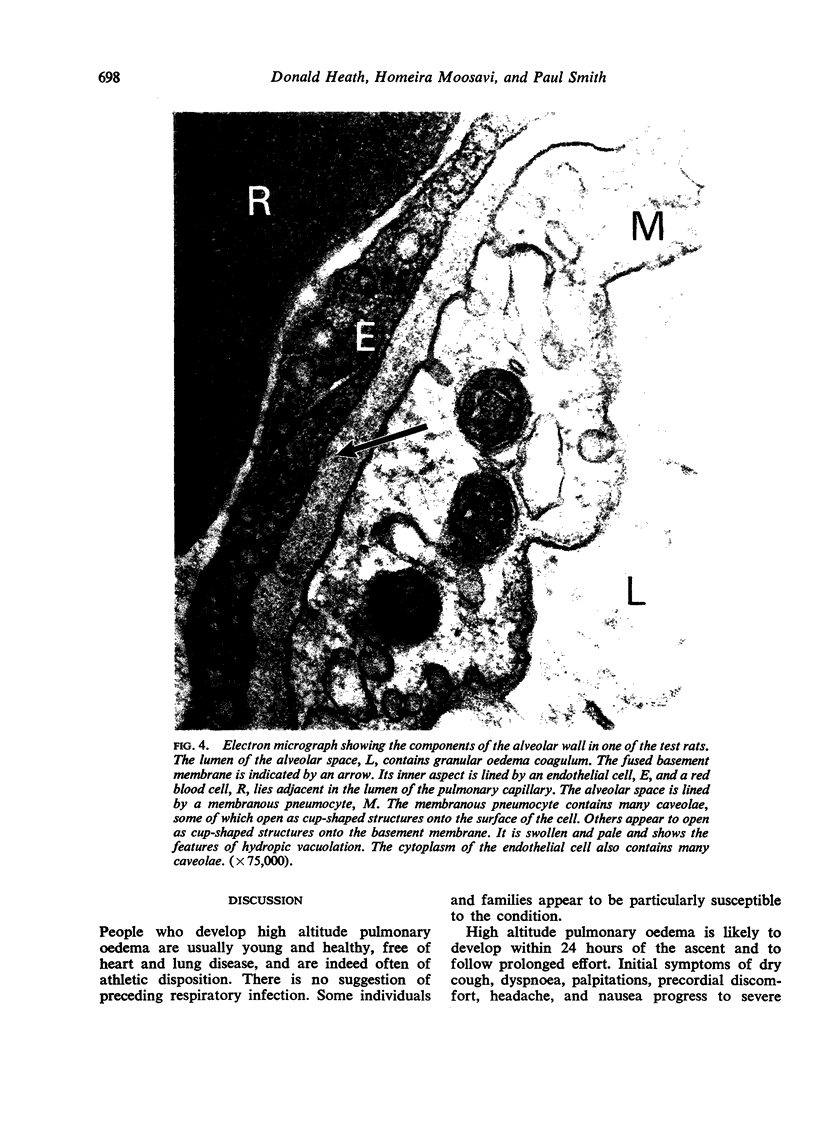
Heath, D., Moosavi, H., and Smith, P. (1973).Thorax, 28, 694-700. Ultrastructure of high altitude pulmonary oedema. When rats are exposed for 12 hours to simulated high altitude corresponding to the summit of Mount Everest, they develop ultrastructural changes in the lungs. These consist of the formation and protrusion of multiple endothelial vesicles into the pulmonary capillaries. It seems likely that they are associated with the development of high altitude pulmonary oedema.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Hayes J. A., Shiga A. Ultrastructural changes in pulmonary oedema produced experimentally with ammonium sulphate. J Pathol. 1970 Apr;100(4):281–286. doi: 10.1002/path.1711000407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay J. M., Smith P., Heath D. Electron microscopy of Crotalaria pulmonary hypertension. Thorax. 1969 Sep;24(5):511–526. doi: 10.1136/thx.24.5.511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTICORENA E., TAPIA F. A., DYER J., SEVERINO J., BANCHERO N., GAMBOA R., KRUGER H., PENALOZA D. PULMONARY EDEMA BY ASCENDING TO HIGH ALTITUDES. Dis Chest. 1964 Mar;45:273–283. doi: 10.1378/chest.45.3.273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyrick B., Miller J., Reid L. Pulmonary oedema induced by ANTU, or by high or low oxygen concentrations in rat--an electron microscopic study. Br J Exp Pathol. 1972 Aug;53(4):347–358. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]