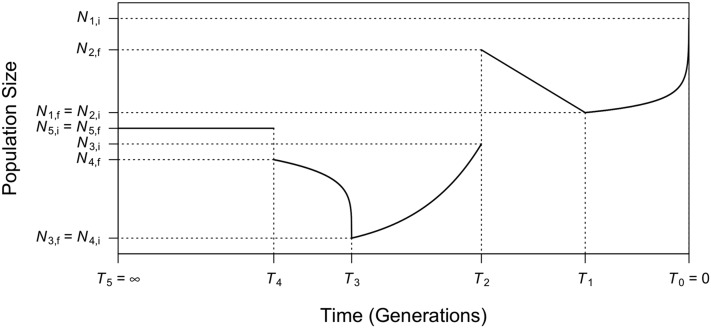
Figure 1.
Illustration of an example of a generalized demographic model as introduced in the first section of Materials and Methods. This model consists of five epochs (starting from the present on the right): (1) faster-than-exponential () growth (forward in time) from to between and (2) linear decline (a special case of generalized decline when ) from to between and (3) exponential growth (a special case of generalized growth when ) from to between and (4) slower-than-exponential () decline from to between and and (5) constant population size (a special case of generalized growth when ) at starting from , which lasts indefinitely backward in time (). The ending population size of the previous epoch is not necessarily the beginning population size of the next epoch (e.g., , ), corresponding to an instantaneous population size change at that time.