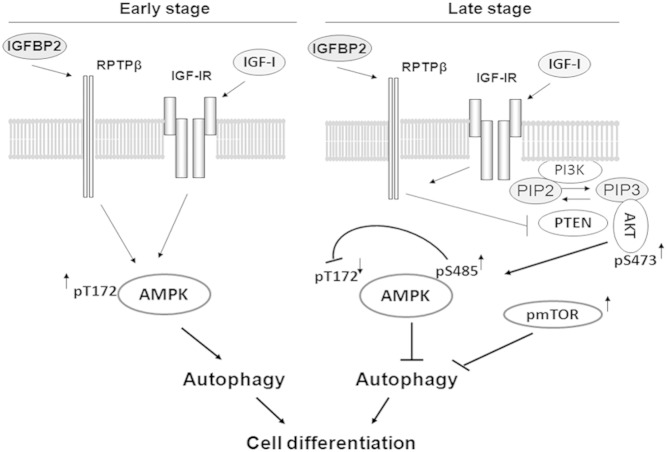
Figure 7.
Biphasic regulation of AMPK and autophagy is required for osteoblast differentiation. At the early stage of differentiation, IGF-I and IGFBP-2 stimulate AMPK activation via IGF-I receptor and RPTPβ dependent pathways, respectively, resulting in activation of autophagy. This early activation of AMPK and autophagy is required for optimal osteoblast differentiation. At the late stage of differentiation, IGF-I and IGFBP-2 stimulate RPTPβ oligomerization and inactivation, leading to inactivation of PTEN and activation of AKT (S473 phosphorylation). Activation of AKT stimulates AMPK S485 phosphorylation, leading to the suppression of AMPK activation (reduction of T172 phosphorylation) and the termination of autophagy. Activation of mTOR at this stage further suppresses autophagy via activation of ULK S757. These signaling events at the late stage are also essential for optimal osteoblast differentiation.