FIGURE 5.
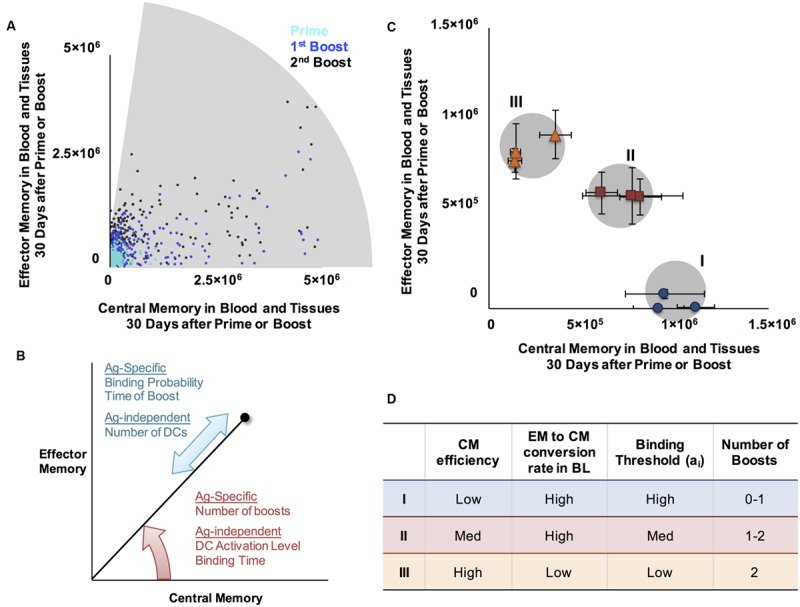
A range of CM/EM ratios and memory population sizes can be reached following prime and boost. (A) Shaded region represents EM/CM ratios and memory population sizes achieved at the memory time point, 30 days after priming event (cyan, same data as Figure 3A), prime and boost (blue), or prime and two boosts (black) for CD4+ memory T cells. (B) Summary of mechanisms affecting EM/CM ratio (red arrow) and memory population size (blue arrow) as determined by sensitivity analysis. (C) Generating memory populations with specific sizes and EM/CM ratios (skew). We identified three desired memory populations (I, II, and III and gray circles). We then designed vaccination simulations to generate these desired memory populations ratios and sizes. Simulated T cell populations representing the closest match for each desired memory population are plotted in Memory Design Space, on the same axes for comparison: blue dots (desired population I), red squares (population II), and orange triangles (population III). Error bars represent SEM (n = 10). (D) Summary of approximate parameter values to achieve specified positions in Memory Design Space. The Ag-specific and Ag-independent parameters noted here were varied simultaneously to achieve desired populations. The ranges over which each parameter was varied are as follows: CM efficiency 0.1-10, EM to CM conversion in BL 0-0.188 (baseline value), binding threshold: 30-300, number of boosts: 0-2. For each of the desired memory population, three independent parameter sets that generated populations with desired characteristics were identified. Exact parameter values are given in Supplementary Table 2.
