FIGURE 5.
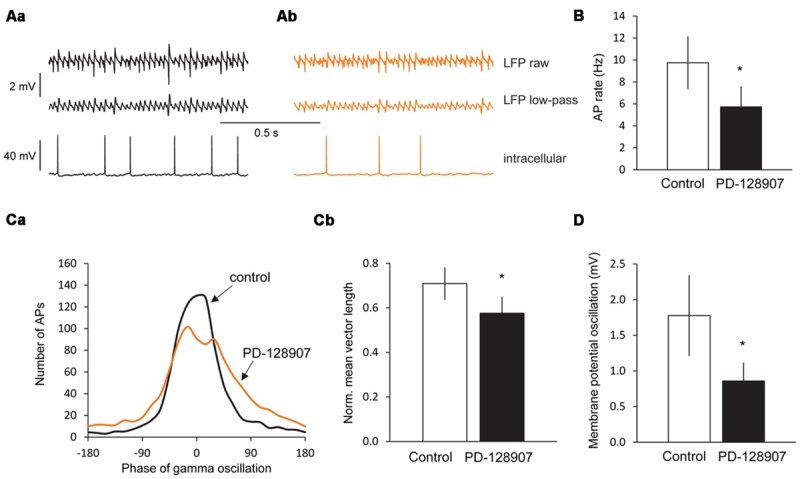
Dopamine D3 receptors decrease the firing rate, firing synchrony and membrane potential oscillations in CA3 pyramidal cells during gamma oscillations. (Aa) LFP recordings from the CA3 pyramidal cell layer (top), the low-pass (100 Hz) filtered LFP signal (middle) and the corresponding intracellular recording from a CA3 pyramidal cell (bottom) after the induction of gamma oscillations by ACh and Physo. (Ab) Effects of the selective D3 receptor agonist PD-128907 (10 μM) on the LFP recordings (top) and the corresponding intracellular recordings from a CA3 pyramidal cell (bottom). (B) Bars summarize the firing rates before and after PD-128907 application. (Ca) Phase histograms of action potentials (APs) before and after PD-128907 application. The average curve for all measured cells is shown (n = 7). In every cell, 1000 APs were analyzed. 0° represents the troughs of the gamma cycles after low-pass filtering. PD-128907 broadened the distribution of APs during the gamma cycle. (Cb) Bars summarize the mean vector lengths (r) before and after PD-128907 application. r = 1 would mean that all cells fired all APs at the very same phase with maximal synchrony; r = 0 that all APs were equally distributed over the gamma cycle. (D) Bars summarize the peak-to-peak amplitude of membrane potential oscillations from CA3 pyramidal cells before and after PD-128907 application. ∗p < 0.05 compared to the 10-min baseline period before PD-128907.
