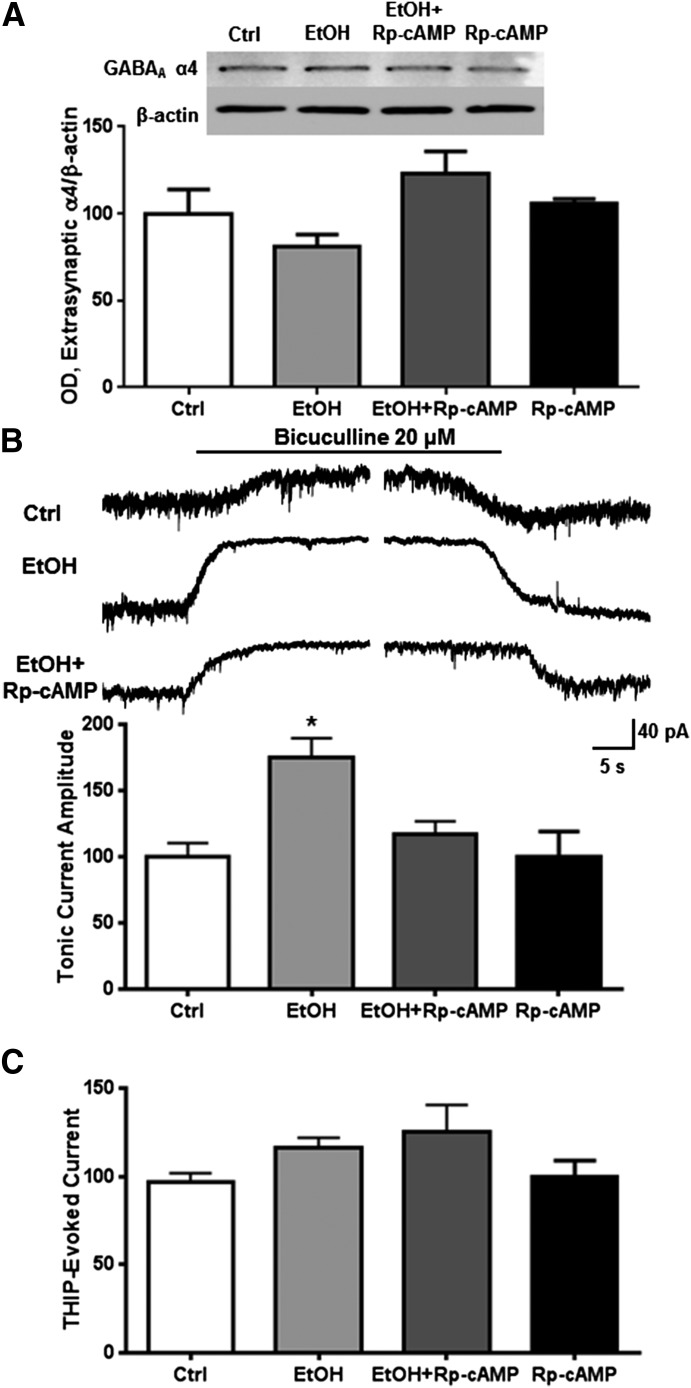
Fig. 1.
PKA mediates ethanol-induced increases in tonic current activity. Cortical neurons were exposed to vehicle, ethanol (50 mM), and/or Rp-cAMP (50 μM) for 1 hour followed by either subsynaptic fractionation and western blot analysis or whole-cell patch clamp recording. (A) There was no effect of ethanol and/or PKA inhibition on extrasynaptic α4 subunit abundance. (B) Ethanol exposure significantly increased bicuculline-blocked current, an effect that was prevented by inhibiting PKA. (C) There was no effect of ethanol or PKA inhibition on THIP-evoked current. * P < 0.05, one-way ANOVA Bonferroni post-test, n = 7–12.