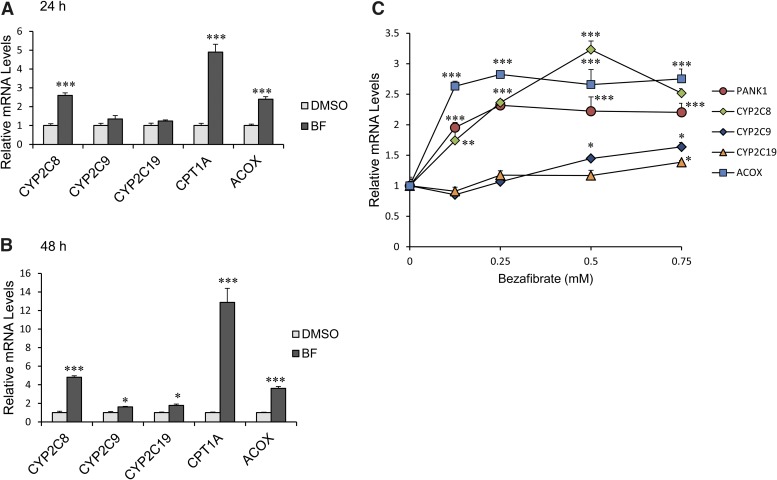
Fig. 2.
Human CYP2C8 mRNA levels were induced by BF in primary human hepatocytes. (A–C) represent human hepatocytes isolated from at least three different donors, as shown in Table 2. CYP2C8, CYP2C9, and CYP2C19 mRNA expression in cultured human hepatocytes following treatment with 0.5 mM BF for (A) 24 and (B) 48 hours were analyzed by quantitative PCR. CYP2C8 mRNA was significantly increased 24 and 48 hours after BF (P < 0.001) compared with minimal increases. *P < 0.05 in CYP2C9 and CYP2C19 mRNA 48 hours after BF compared with DMSO control. CPT1A and ACOX, known PPARα target genes, were dramatically increased by BF. ***P < 0.001 compared with DMSO control (Student’s t test). (C) Human primary hepatocytes were treated with 0.125, 0.25, 0.5, and 0.75 mM BF for 48 hours. Total RNA was extracted, and gene expression was examined by quantitative PCR. Each donor sample was analyzed in triplicate, and data indicate the mean ± S.E.M. of at least three different donor preparations. *P < 0.05 compared with DMSO control; **P < 0.01 compared with DMSO control; ***P < 0.001 compared with DMSO control (one-way analysis of variance followed by Tukey’s test).