Figure 1. ASK3 binds to WNK4 and induces WNK4 phosphorylation in cells.
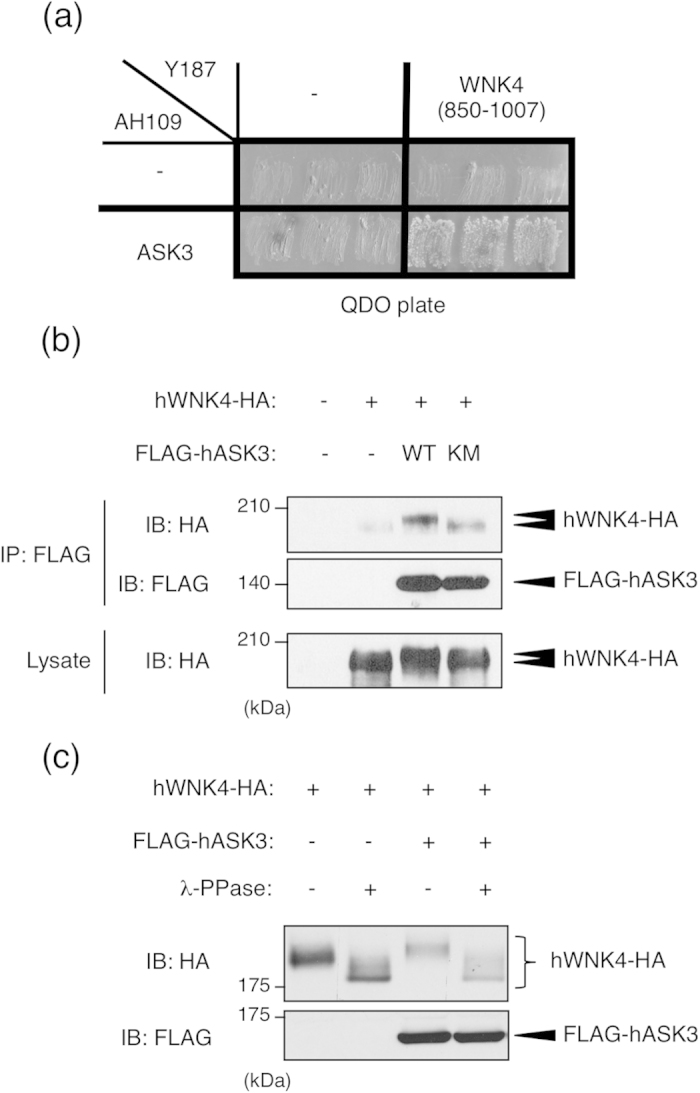
(a) Interaction between ASK3 and WNK4 in yeast. Yeast strain Y187 containing a plasmid encoding human WNK4 (850–1007) fused to the GAL4 transcriptional activation domain was mated with the yeast strain AH109 containing a plasmid encoding human ASK3-KM fused to the GAL4 DNA-binding domain. The mated yeast was able to survive on restriction medium (QDO). (b) Interaction between ASK3 and WNK4 in mammalian cells. HEK293A cells were transiently transfected with FLAG-tagged human ASK3 (FLAG-hASK3) wild type or human ASK3 kinase-inactive mutant (hASK3-KM) and HA-tagged human WNK4 (hWNK4-HA). Cells were lysed at 48 h after transfection. Lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-FLAG antibody beads and subjected to immunoblotting (IB). Co-immunoprecipitated WNK4 was detected only in the co-transfected cells. Full-length blots are presented in Supplementary Fig. S5a. (c) The ASK3-dependent mobility shift of WNK4 band is due to phosphorylation. HEK293A cells were transiently transfected with FLAG-hASK3 and hWNK4-HA. Cells were lysed at 48 h after transfection. Lysates were divided, and a portion was treated with λ-phosphatase (λ-PPase) for 30 min at 30 °C. The reaction was terminated by the addition of SDS sample buffer, and samples were subjected to IB. Bands corresponding to both WNK4 that was expressed alone and WNK4 that was co-expressed with ASK3 were shifted lower and ran at the same position. Full-length blots are presented in Supplementary Fig. S5b.
